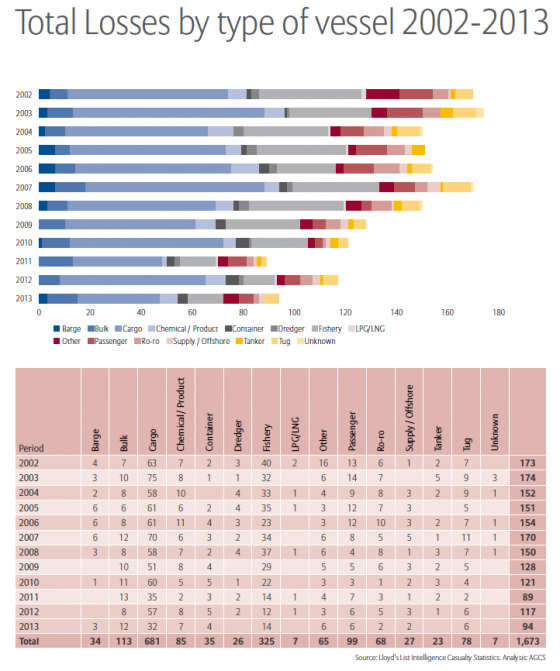
The marine industry continued to see a steady decline in the number of large ships losses globally since 2002, with 94 ships lost in 2013, down 20% from 117 reported in 2012, according to a study by Allianz.
The “Safety and Shipping Review 2014” by Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty found that of ships lost, the largest number, 32, were cargo vessels; 14 were fishing vessels; and 12 were bulk shipments. Only six passenger ships were lost, the survey found. The most common cause of losses in 2013, and over the last 12 years, was foundering (sinking or submerging). The demise of 69 ships accounted for nearly three-quarters of all losses—with bad weather a significant driver.
Worldwide there were 1,673 losses from Jan. 1, 2002-Dec. 31, 2013, with an average of 139 per year. The top geographic area for losses has been South China, Indo China, Indonesia and Philippines. The area including British Isles, North Sea, English Channel and Bay of Biscay is still ranked fourth, despite improvement. With 45 losses overall, the U.S. eastern seaboard improved in 2013, dropping out of the top 10 regions.
According to the study, January is the worst month for all casualties in the Northern Hemisphere. There were 23% more losses in January compared with the quietest month, June. In the Southern Hemisphere July sees 41% more losses than April.
The majority of losses are caused by machinery damage, the reason for most losses in marine insurance. Statistics from the International Union of Marine Insurance (IUMI) report that 40% of hull claims are machinery damage and account for 20% of costs.
The review found that while piracy is still a threat, it has also subsided. Piracy at sea reached its lowest levels in six years, with 264 attacks recorded worldwide in 2013, a 40% drop since Somali piracy peaked in 2011. Fifteen incidents were reported off Somalia in 2013, including Gulf of Aden and Red Sea incidents, down from 75 in 2012, and 237 in 2011 (including attacks attributed to Somali pirates in Gulf of Aden, Red Sea and Oman).
According to the study: “The very real threat of piracy for ships operating in the Gulf of Aden reached the general public last year as the Hollywood Oscar-nominated blockbuster Captain Phillips was released. Tom Hanks played the lead as the master of the pirated Mærsk Alabama, broadcasting the piracy problem to a much wider audience and raising awareness of its consequences. The steps that the international maritime community has taken to reduce the threat of piracy in the Gulf of Aden have been extremely successful with the number of ships seized and hostages taken in 2013 significantly down on 2012.”
Lower losses overall were attributed to a number of factors including increased regulation, which has helped the maritime industry improve its safety record. Because the quality of operations varies in different regions, however, there is a big need for universal regulations on ship safety to reduce the risk of casualties and loss of life, the survey concluded.