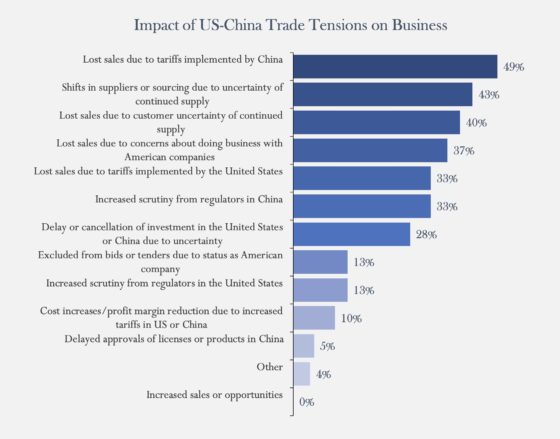
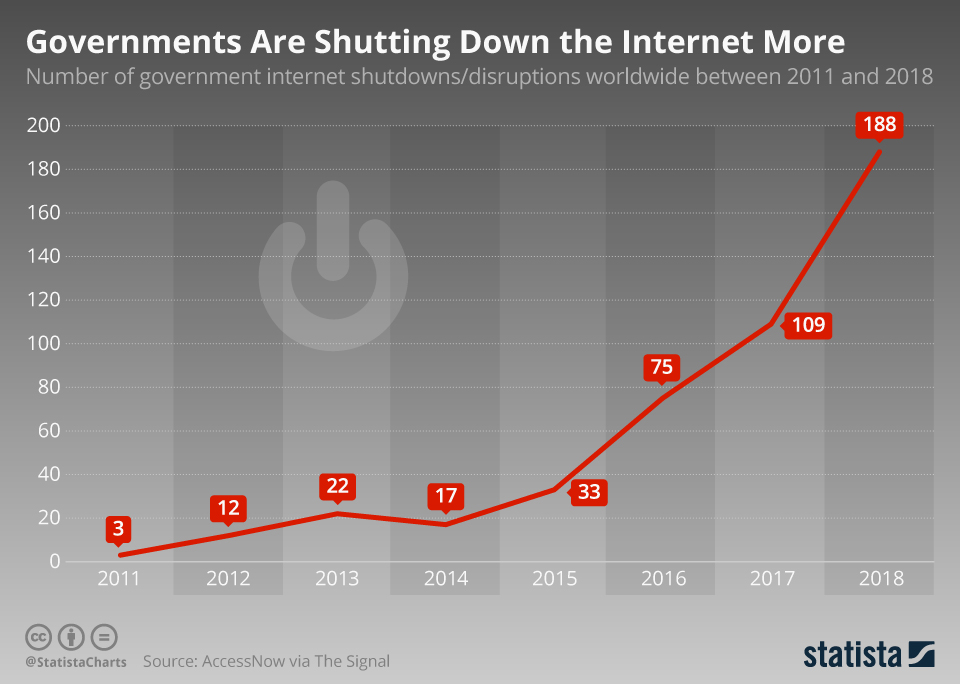
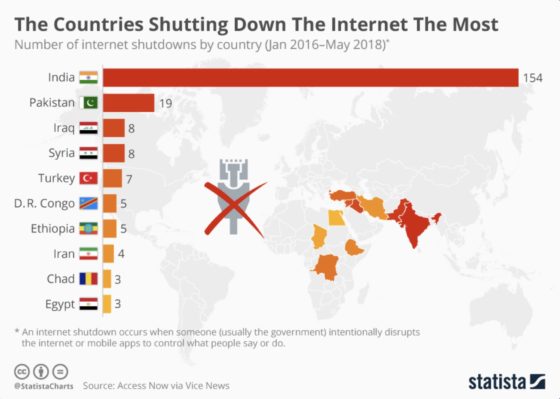
The novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV continues to spread throughout China and other countries, seriously impacting business operations around the world. As governments and companies act to protect their citizens, operations and employees at home and abroad, these actions threaten to produce business interruptions, travel risks and other effects that could be detrimental to business continuity.
On January 30, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the virus a global emergency, meaning that it is a threat beyond China, after more cases have appeared in other countries around the world.
According to the New York Times, the WHO has only made such a declaration five times since 2005. The virus has killed more than 400 people (including 2 outside mainland China) and has infected more than 20,000 in more than 25 countries.
In addition to the cancellation of major public events in China (including celebrations of Chinese New Year), many international businesses have curtailed their operations there since the outbreak. According to Bloomberg, this includes Starbucks (which closed more than half of its shops), Toyota (which stopped production), McDonald’s and KFC (which both closed restaurants), and Disney (which closed its resort in Shanghai), among others.
Some international companies have instructed their employees to work from home to limit exposure as the virus spreads, and Amazon, Microsoft and other tech companies also limited employee travel to and from China.
China has maintained mass quarantines of areas with high number of infections, including Wuhan, the origin of the outbreak, and some other countries are also taking extraordinary steps to limit the virus’s spread. Last week, Russia sealed its entire border with China and cancelled all trains between the countries except for a single train line between Moscow and Beijing. Japan is currently quarantining more than 3,000 people on a ship after a passenger tested positive after departing the ship, while the United Kingdom has advised its citizens to leave China. And the United States issued a proclamation suspending entry for non-citizens who spent 14 or more days in China before attempting to enter the United States.
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) stated that the risk for people in the United States is “considered low at this time,” with elevated risk for individuals who may have increased exposure—such as healthcare workers and others in close contact with patients with the virus. However, companies should still act to protect their operations and employees, especially if operations require international travel and if supply chains depend on Chinese business continuity. Here are three approaches to limit risk from the coronavirus:
1. Take Travel Precautions
The CDC has recommended avoiding all non-essential travel to China, and the U.S. State Department has asked people not to travel to China. If travel is essential, the CDC suggests avoiding contact with sick people, any animals, animal markets or products made from animals. If traveling employees are older, they should take extra precautions, since, “older adults and people with underlying health conditions may be at increased risk.”
2. Develop a Response Plan
Medical and travel security services firm International SOS also recommended that businesses have regularly-updated and evaluated business continuity plans in place to ensure smooth response to incidents like disease outbreaks. The Institute of Risk Management South Africa (IRMSA) recommended preparing a specifically-focused “Pandemic Preparedness Plan” or updating previously prepared plans to reflect current circumstances to ensure business continuity.
IRMSA also suggested creating a group within the company, chaired by a senior staff member, able to make quick executive decisions for the organization in response to any coronavirus-related impact to the business and prepare decision-making processes for future incidents.
3. Consult Reputable Information Sources
Relying solely on reputable news sources, like government disease control agencies and reliable media, can help when evaluating and taking courses of action to reduce risk. Conspiracy theories about the coronavirus have spread rapidly, including misinformation about its source, how to protect against or treat infections, and the number of people affected. Misinformation has also resulted in discrimination against Chinese-linked businesses and people of Chinese heritage, as well as East Asian people in general. Disseminating clear, reputable information to all employees, especially those traveling, can reduce risk of infection and impact on business operations.