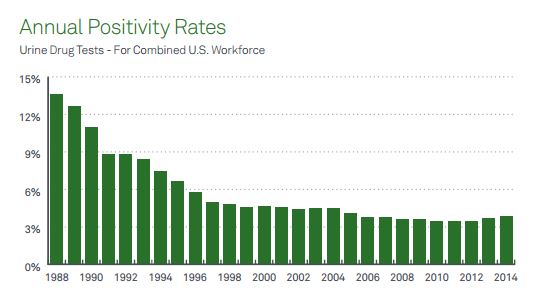
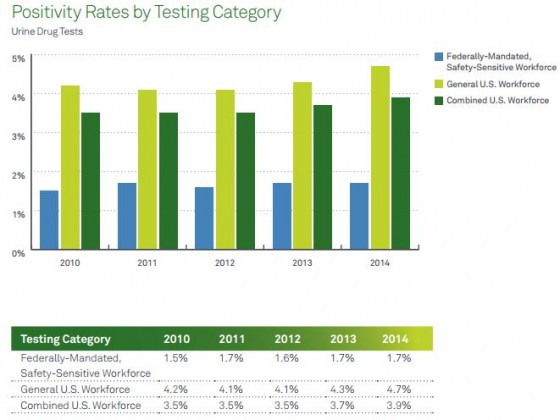
Organizations in the United States that tested employees for drugs saw a 9.3% jump in the number of positive drug tests for illicit drugs in the general workforce, to 4.7% in 2014 from 4.3% in 2013, according to data from Quest Diagnostics. These results may mark a rising trend, as 2013 was the first year since 2003 in which the overall positivity rate for about 1.1 million tests increased in the general U.S. workforce. The analysis shows a potential reversal of a decades-long decline in the abuse of illicit drugs in the U.S. workforce, Quest said.
“American workers are increasingly testing positive for workforce drug use across almost all workforce categories and drug test specimen types. In the past, we have noted increases in prescription drug positivity rates, but now it seems illicit drug use may be on the rise, according to our data,” Dr. Barry Sample, director of science and technology at Quest Diagnostics Employer Solutions, said in a statement.
“These findings are especially concerning because they suggest that the recent focus on illicit marijuana use may be too narrow, and that other dangerous drugs are potentially making a comeback.”
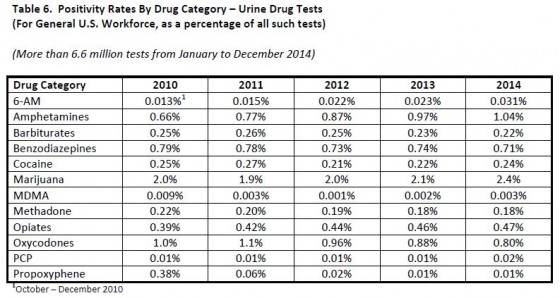
While marijuana continues to be the most commonly detected illicit drug, others include cocaine, methamphetamine and heroin, Quest reported, noting that across all specimen types, the positivity rate for amphetamines is now at the highest levels on record and the positivity rate for methamphetamine is at its highest level since 2007. Amphetamines make up the category that includes both prescription amphetamine drugs like Adderall as well as methamphetamine. The positivity rate for 6-acetylmorphine, or 6-AM, a specific marker for heroin, doubled in the general U.S. workforce between 2011 and 2014, According to Quest.
In urine drug test data from two states with recreational marijuana-use laws, Colorado and Washington, the marijuana positivity rate increased 14% and 16%, respectively, in the general U.S. workforce between 2013 and 2014. This roughly paralleled the national average of 14.
3%. By comparison, between 2012 and 2013, the marijuana positivity rate increased 20% and 23% in Colorado and Washington, respectively, compared to the national average of 5%, Quest said.
“We were surprised that marijuana positivity increased at about the same rate in Colorado and Washington as the rest of the United States in 2014, particularly given the sharp increases in the marijuana positivity rate in both of these states in the prior year,” Dr. Sample said. “It’s unclear if this data suggest a leveling off in marijuana use in these particular states or if some other factor is at work. We also find it notable that the national marijuana positivity rate increased as much as it did in 2014, and question if this means that people are more accepting and therefore more likely to use marijuana recreationally or for therapeutic purposes than in the past even in states where marijuana’s use is not clearly sanctioned by state laws. This will be an important area of continued analysis given the national debate about the legality and health impacts of recreational and medicinal marijuana use.”