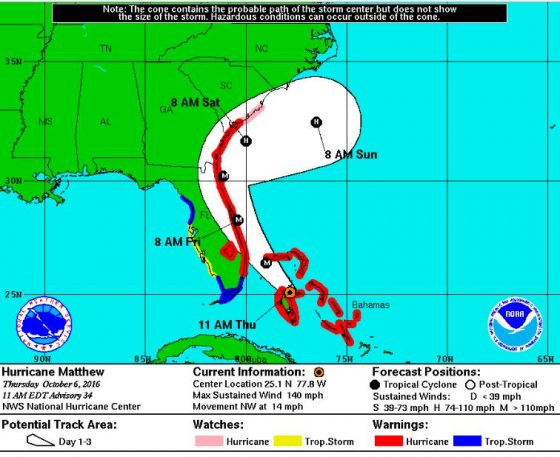
Rebounding to Category 4 hurricane classification, Matthew now has winds up to 140 miles per hour and has caused at least 28 deaths in three Caribbean countries. It is heading for the southeastern U.S., where four states—Florida, Georgia, South Carolina and North Carolina—have issued a state of emergency and evacuation orders in coastal regions.
Matthew was a Category 4 hurricane through Tuesday, was downgraded to a Category 3 early on Wednesday, and has now returned to Category 4 strength today, according to the U.S. National Hurricane Center (NHC).
Florida Gov. Rick Scott issued a warning on Thursday urging those in evacuation zones to leave immediately. “Based on the current forecast, the heights of storm surge will be above ground. Waves will be crashing on roofs. Homes will be destroyed,” he tweeted in both English and Spanish on Thursday morning.
“Time is up, Hurricane Matthew is approaching Florida. If you are in an evacuation zone, leave now,” he said in a statement. “To everyone on Florida’s east coast, if you are reluctant to evacuate, just think of all the people the hurricane has already killed. You and your family could be among these numbers if you don’t take this seriously.”
Scott said that so far more than 4,000 National Guard members have been activated to help with evacuations and sheltering. He tweeted that as of 6:00 a.m., more than 3,000 people were in about 60 shelters. The state offers a mobile app to help those in flood-prone areas find the nearest shelter and also avoid traffic congestion.
A state of emergency has been declared by Georgia’s governor for 13 coastal counties. South Carolina’s governor declared a state of emergency and has begun coastal evacuations that may affect up to 1 million people. Because of heavy traffic, lane reversals on some highways are in effect, and schools and government offices in 25 South Carolina counties are closed today. North Carolina’s governor has declared a state of emergency for more than 50 counties and issued a mandatory evacuation order for Ocracoke Island, AIR Worldwide reported.
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has sent personnel and supplies to all four states, and President Obama is meeting with FEMA officials coordinating the response to Hurricane Matthew at the agency’s headquarters in Washington, D.C.
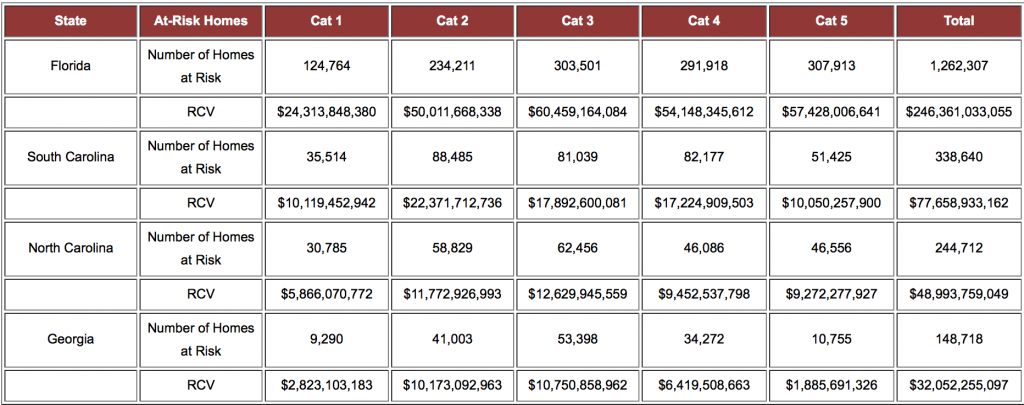
According to CoreLogic, a Category 3 storm hitting Miami could potentially damage 176,000 homes at a reconstruction cost value (RCV) of about $3.8 billion.
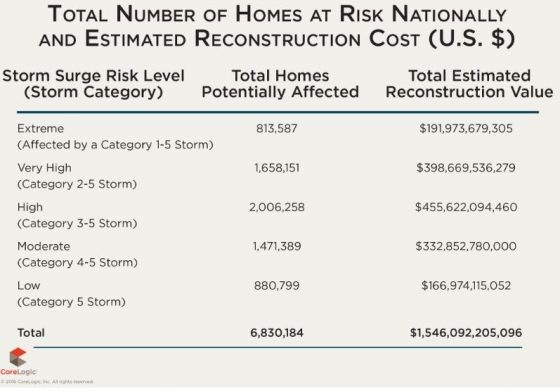
CoreLogic’s Storm Surge Risk Report estimates that more than 6.8 million homes located along the Gulf and Atlantic coasts are at risk of storm surge damage, with a total RCV of about $1.5 trillion.The length of coastline, coastal elevation and density of residential development all contribute to the risk of storm surge flooding.
According to CoreLogic, the total number and total value of residential properties for the four states currently bracing for Hurricane Matthew are: