The following article is part of a continuing blog series that will explore ideas, concepts, discussions, arguments and applications associated with the field of enterprise and strategic risk management.
In my previous article, I made the point that the public discussion of reputational risk lacks a set of common standards or definitions. This lack of consistency allows organizations to interpret or define the concept of reputational risk in very different ways. For some, reputation is beginning to be viewed as something like the “risk of risks” in the same way people are starting to discuss the concept of the “internet of things.” I questioned whether reputation or brand is actually a risk or a residual event stemming from other extenuating risk domains or actions.
Upon further reflection and discussions with academics and risk professionals who are thinking carefully about this issue, I would go further now to suggest that reputation or brand risk involves perceived or real human behaviors that are, to some extent, measured against societal, economic or moral standards. The adherence or deviation from established standards generates the basis for the risk, and the variability from the standard influences the duration of the outcome.
The bigger question is: What impact does reputational risk have on economic performance when possibly mitigated by the existence of a robust enterprise or strategic risk management methodology? Is the data available to see the “correlates” between a reputational risk event that trigger or influence operational key process indicators like EBIT, ROA, ROE and share price (public or private)?
What we do know from the Aon 2015 Global Risk Management Survey is that business leaders are concerned about reputational risk in general and the possible linkages with other hazard and operational risks within their organizations.
The respondents to the survey said that they worried that a reputational risk event would significantly impact financial performance.
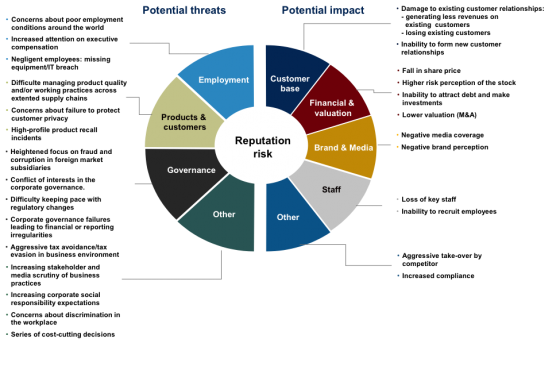
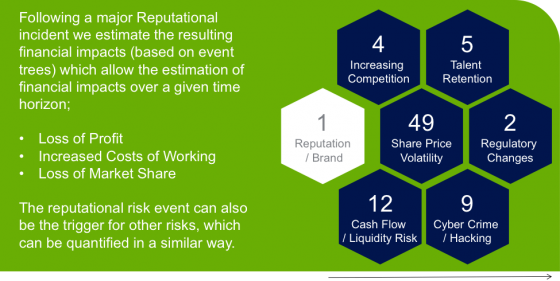 If reputation/brand risk was identified as a precipitating event, the respondents identified regulatory change, increasing competition, talent retention, cash flow/liquidity and share price volatility as “follow on” risk consequences. In effect, reputation/brand risk might constitute a “gateway” risk, where other related “follow on” risk consequences are triggered and serve to increase the overall volatility/impact of the reputation event.
If reputation/brand risk was identified as a precipitating event, the respondents identified regulatory change, increasing competition, talent retention, cash flow/liquidity and share price volatility as “follow on” risk consequences. In effect, reputation/brand risk might constitute a “gateway” risk, where other related “follow on” risk consequences are triggered and serve to increase the overall volatility/impact of the reputation event.
Another way to view the data is to see what events could trigger a reputation event.
 In this case, the survey respondents identified nine non-correlated risks that could precipitate a reputation/brand event. Here social media plays an important role.
In this case, the survey respondents identified nine non-correlated risks that could precipitate a reputation/brand event. Here social media plays an important role.
The speed by which information, accurate or not, is transmitted, consumed and iterated across the nine risk categories may have a material impact on the basis and duration of the reputation/brand event. There is also an error component associated with social media.
How many times have we witnessed an initial media report of a brand damaging event that turns out to be prematurely reported and the facts distorted, only to be corrected in a later reporting cycle?
Next up: Fat vs. thin tail distributions.