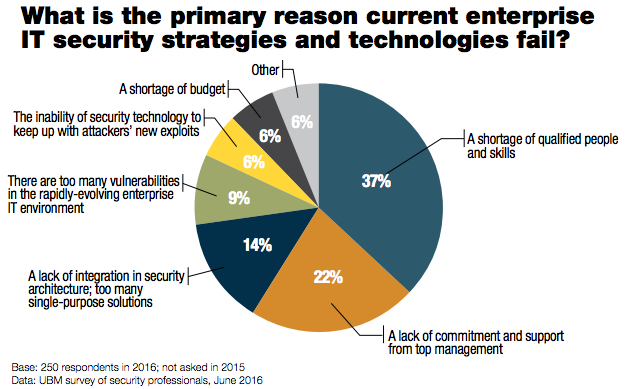
LAS VEGAS—At this week’s Black Hat conference, some information security professionals turned to a key issue to control enterprise-wide cyberrisk: hacking humans.
As phishing continues to be one of the top threats for businesses, hackers and security professionals here continue to try and make sense of why this threat vector is so successful and how to better defend against these attacks.
In a session called “Blunting the Phisher’s Spear: A risk-based approach for defining user training and awarding administrative privileges,” Professor Arun Vishwanath presented some of his research on the “people problem” of cybersecurity, proposing a new model for quantifying the cyberrisk posed by individuals within the enterprise and tailoring training to best mitigate the risk they pose. While many corporate training programs stage fake phishing emails and then lecture those who fail, he said, this model continues to be ineffective, as proven by the increase in these attacks and their efficacy across all industries. People are not the problem, Vishwanath asserted, rather it is in our understanding of people.
Vishwanath and his colleagues have come up with a model to explain how users think, the Suspicion, Cognition, Automaticity Model (SCAM). Faulty ideas about cybersecurity practices, popular myths and other irrational beliefs lead to illogical and unsafe practices. Automatic behaviors also play a significant role in risky behavior, particularly with mobile devices and the ritualistic checking of email – users open messages mindlessly and get so used to clicking links, downloading files or entering credentials that they do not really factor logic into these decisions.
Based on this model of why individuals act in risky ways, he recommends developing a Cyber Risk Index (CRI) based on a short, 40-question survey given to individual employees to evaluate the cyberrisk they specifically pose, which can also be aggregated across divisions, sectors and organizations.
buy silvitra online https://royalcitydrugs.com/silvitra.html no prescription
As the results highlight different areas of weakness that lead to the employee’s risky behaviors, the CRI can dictate the best ways to that individual and mitigate the risk.
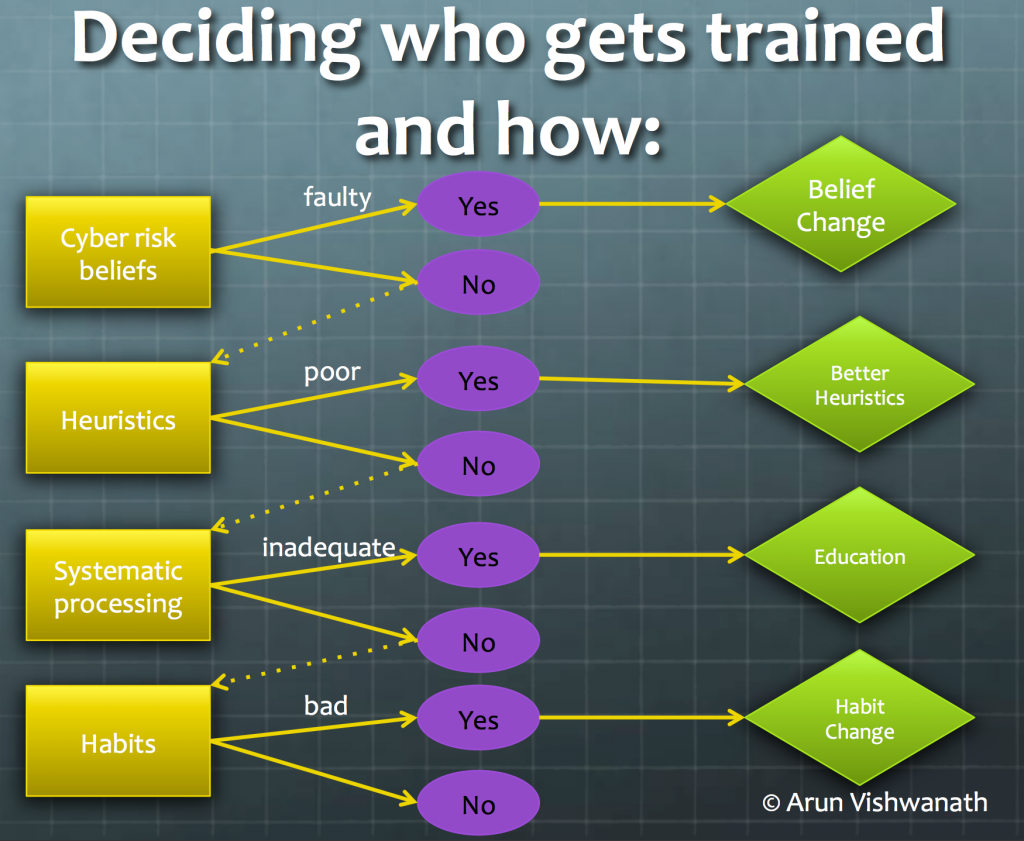 What’s more, this quantitative score of individual cyber hygiene can be used to track changes in risk posture over time and to improve current decision processes regarding privileged access to the organization’s systems to better control data at risk.
What’s more, this quantitative score of individual cyber hygiene can be used to track changes in risk posture over time and to improve current decision processes regarding privileged access to the organization’s systems to better control data at risk.
Check out Dr. Vishwanath’s whitepaper for more on this approach.