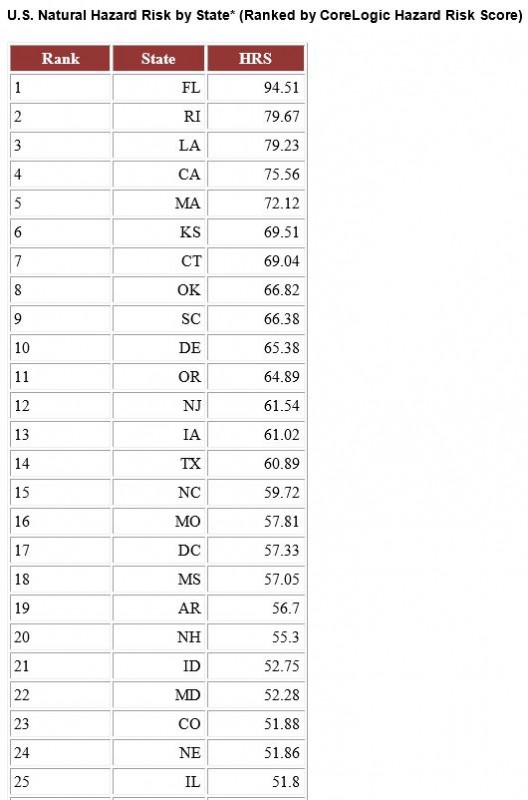
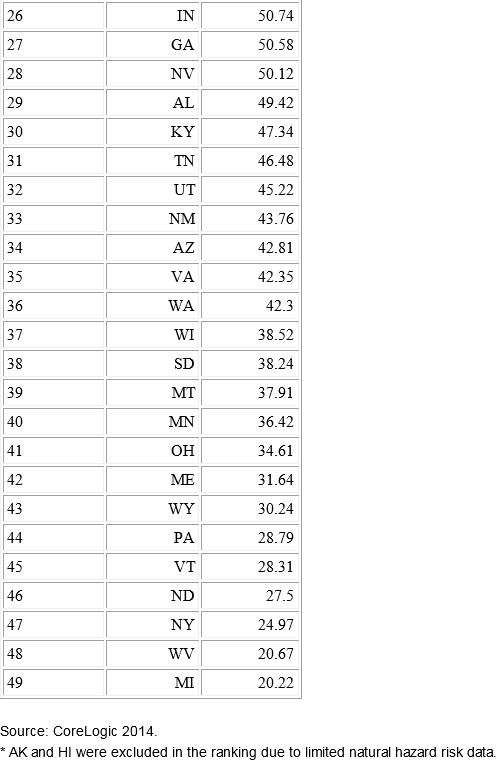
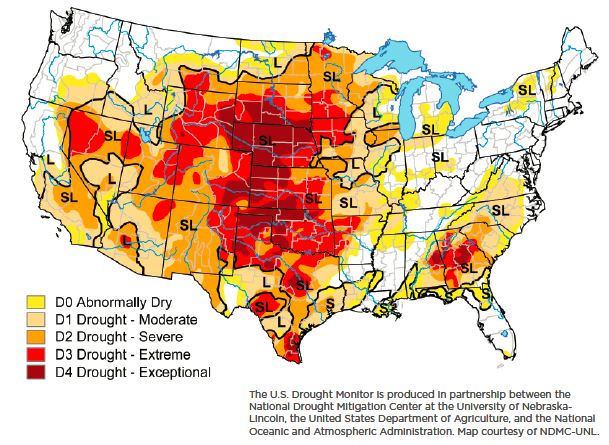
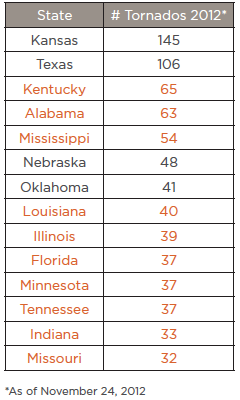
While most natural hazards occurring in the United States last year saw average or below average activity, the exceptions were flood and wind, according to the CoreLogic report Natural Hazard Risk Summary and Analysis, released today.
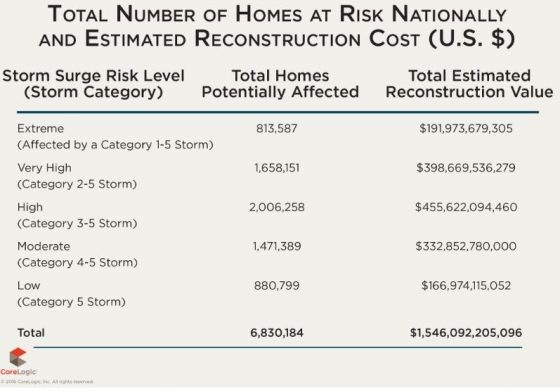
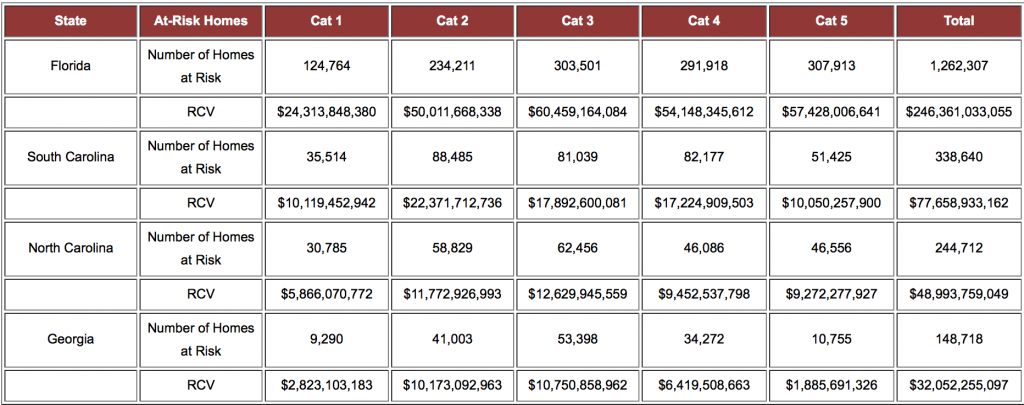
Severe flood events driven by substantial rainfall were the dominant natural hazards, with Louisiana and North Carolina floods being the major loss contributors. As in 2015, hurricanes and tropical storms in 2016 continued to cause inland flooding through increased and intense rainfall—even when not making landfall, according to the report.

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) said there were 12 individual weather and climate disaster events in the U.S. with losses exceeding $1 billion in 2016.
According to the report:
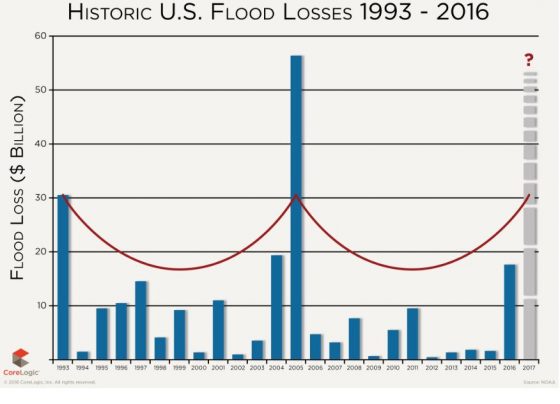
- Based on NOAA and CoreLogic analysis, the overall flood loss in 2016, driven by six, 1,000-year plus rain events, was approximately $17 billion, which is six times greater than the overall flood damage experienced in 2015.
- The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) recorded 943 earthquakes of magnitude 3.0 or greater in 2016, with more than 60 percent of these earthquakes located in Oklahoma.
- The National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC) reported a total of 5,415,121 acres burned from 62,864 separate fires in 2016.
buy arimidex online achievephysiorehab.ca/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/jpg/arimidex.html no prescription pharmacy
While the total acres burned in 2016 fell below the 10-year average, significant losses occurred, with thousands of homes in California and Tennessee destroyed by several smaller fires that burned in populated areas.
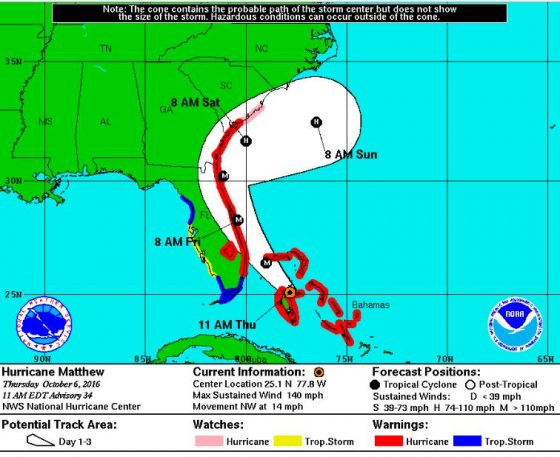
- Wind activity in 2016 was slightly above average, due in large part to strong winds brought by Hurricane Matthew.
buy mobic online achievephysiorehab.ca/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/jpg/mobic.html no prescription pharmacy
- Hail activity in 2016 was near the average, and Texas experienced the worst of this natural hazard.
- Tornado activity in 2016 was near average compared with previous years.
- Hurricane Matthew developed late in the year and grew to a Category 5 storm, resulting in substantial damage along the southeastern seaboard.
- There were below-average levels of tropical cyclone activity in the western North Pacific Basin encompassing East and Southeast Asia in 2016.
However, 2016 became known as the year without a winter. Nine winter storms impacted the U.S. in 2016, the most notable being the late-January winter storm in New York.
“History has continually shown us that it is impossible to determine exactly when or where the next wildfire, flood or earthquake will strike, which is why preparedness, response and post-loss assessment are paramount,” CoreLogic said.