Manufacturing companies face a serious threat from cyber criminals. According to IBM’s latest intelligence index, theirs is now the second-most targeted sector, after attack numbers increased significantly year-on-year. This heightened risk is compounded by increased vulnerability: the connectivity that manufacturers have embraced to bring about greater operational efficiencies is accompanied by significant and largely uninsured exposures, such as physical damage arising from cyber incidents or loss of income due to stolen intellectual property.
Part of the vulnerability lies in process control and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. Previously deemed impenetrable, due to their proprietary and highly customised networks, the convergence of these industrial control systems with enterprise infrastructure, particularly web services and ethernets, has created a potentially catastrophic risk. Such connections and the increasing Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can drive through great advantages, but also simultaneously produce weak links that manufacturers can not afford to overlook.
For example, expensive capital assets such as production machines will be retrofitted with technology that allows them to be connected to corporate networks. But they were typically built without the sophisticated measures to afford cyber-protection, or have operating systems that are incompatible with current cyber-security products. All these factors make manufacturers’ industrial control systems particularly vulnerable to cyber-attack.
Physical damage
Physical damage arising from cyberattacks has to date been relatively rare. Early high-profile events, such as claims that Russians hacked into U.S. water treatment facilities to damage pumps, or the Israeli-U.S. ‘Stuxnet’ attack on Iran’s nuclear centrifuges were believed to be state-sponsored.
One of the most underestimated threats to manufacturers is the rogue employee, disillusioned with their employer or falling victim to blackmail. One such attack involved a German steel mill.
online pharmacy
aricept with best prices today in the USA
Hackers, thought to involve a rogue employee, took over its industrial control systems via its enterprise system, preventing employees from shutting down a blast furnace. This caused irreparable damage to expensive equipment and yet physical damage, as well as bodily injury caused by a cyber event, is typically excluded on most policies. The rise of the hackers-for-hire phenomenon further multiplies potential sources of attack, with competing companies looking to use third parties for corporate espionage, for example.
Stolen Innovation
Other rising areas of threat revolve around the significant non-physical assets residing in manufacturers’ information systems. Cyber theft of intellectual property (IP) has been difficult to insure properly, despite the extraordinary value of items such as the technical specifications of a new product, or the composition of a new pharmaceutical. PwC reports that the number of such thefts, notably of product designs, has doubled.
While competition is a big driver of IP cyber theft, risks such as the loss of income due to stolen IP or the legal pursuit of it are not currently insurable. When you consider the degree to which a manufacturer’s value will be directly linked to their IP, this represents a considerable risk but also one where evidencing and quantifying a loss is very difficult.
Cyber attacks are now identified as the leading cause of supply chain stoppages but supply chain risk is also largely uninsured.
online pharmacy
cytotec with best prices today in the USA
Some losses, like business interruption arising from a cyber incident on an IT provider’s network, can sometimes be covered but an interruption caused by a product supplier’s cyber-event typically cannot. Upstream supply risk, associated with liabilities arising from failure to supply goods following an attack, is also difficult to insure.
Market developments
According to research by consultancy BDO USA, 92% of manufacturers cited cyber-security among their top 10 risk concerns in 2016, up 44% from 2013. Another study, however, found only 8% of manufacturers “very confident” in their ability to prevent an IT breach.
This rising risk issue demands action from all parties.
online pharmacy
imuran with best prices today in the USA
Manufacturers must invest further in heightened security and control for their operating technologies, while cyber insurance specialists must continue to develop further sophisticated solutions to more effectively transfer manufacturers’ unique exposures. Insurance carriers are starting to work together more effectively across lines to more sufficiently underwrite the complex cyber risks facing the sector. Failure to respond to this new era of cyber threats and vulnerabilities will leave manufacturers exposed to reputation and physical damage, bodily injury, severe business interruption, loss of intellectual property, and significant financial loss.


 urity industry, noting that, “the defense trails the offense by about five years.” Comparing the newest waves of protection software to a strong rookie pitcher, he said, “A new pitcher may come along and strike everybody out as he goes through the league a few times. But eventually he gets figured out and [hackers] figure it out,” he said. “It needs at least a year of being attacked for real,” to find the gaps in efficiency, and leads to the “the kind of experimentation that will yield better results.”
urity industry, noting that, “the defense trails the offense by about five years.” Comparing the newest waves of protection software to a strong rookie pitcher, he said, “A new pitcher may come along and strike everybody out as he goes through the league a few times. But eventually he gets figured out and [hackers] figure it out,” he said. “It needs at least a year of being attacked for real,” to find the gaps in efficiency, and leads to the “the kind of experimentation that will yield better results.”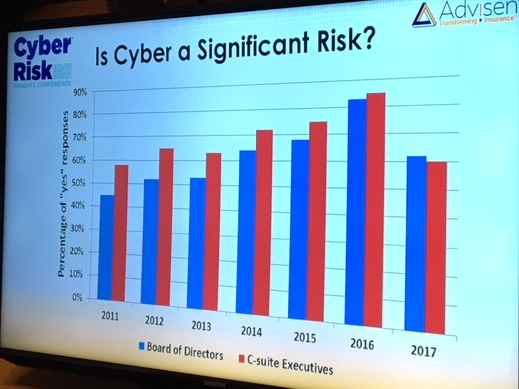 Advisen
Advisen