Improved compliance programs, sufficient resources and board access have meant fewer concerns about personal liability for compliance executives, according to a study by DLA Piper.
In its 2017 Global Compliance & Risk Report, DLA Piper found that 67% of chief compliance officers surveyed said they were at least somewhat concerned about their personal liability and that of their CEOs, which was down from 81% in 2016. And 71% said they made changes to their compliance programs based on recent regulatory events, up from just 21% a year earlier. The study found that globally the compliance function is becoming more independent and prominent in large organizations.
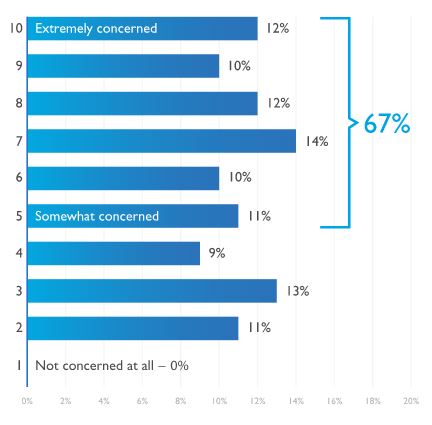
There still remains room for improvement, however, most notably in compliance’s relationship with boards of directors. Directors, surveyed for the first time, were more uneasy, with 82% expressing at least some concern about personal liability. “This is likely related to other findings that show lingering kinks in communications channels and a persistent lack of training for directors. Together, these findings indicate that the relationship between the compliance function and boards needs work—despite efforts taken by organizations to upgrade their compliance program,” DLA Piper said.
In 2016, 77% of compliance executives said they had sufficient resources, clout and board access to support their ability to effectively perform their jobs. This year the number rose to 84% who said they felt that way. The improvement is possibly a reflection of the increased percentage of respondents who had the resources to make changes to their compliance program, compared to 2016, according to the survey.
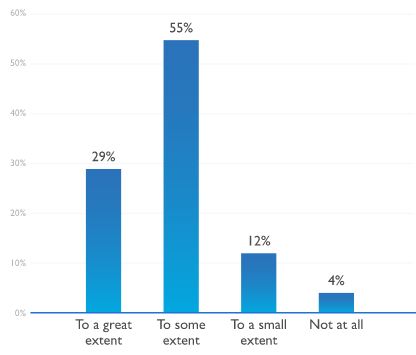
While more respondents said they are increasingly able to affect change, obtain the resources they need and access senior leadership, however, a larger number said their budget was not high enough to accomplish their goals, from 28% in 2016 to 38%.
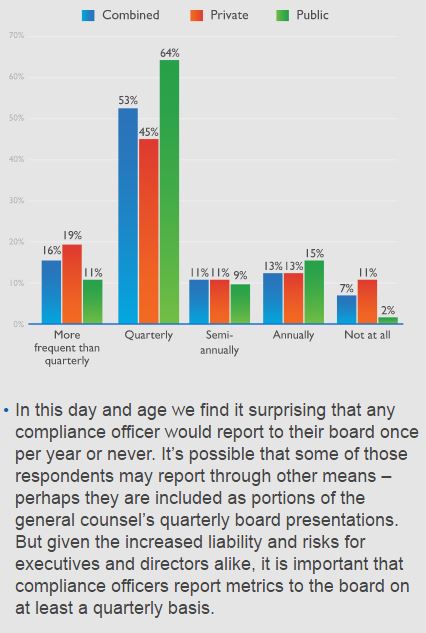
Boards had a different view, with 53% of directors agreeing strongly that their compliance group had sufficient resources, clout and board access. This was compared to just 29% of CCOs, which could indicate that CCOs are not effectively communicating their needs, the company said.
Of concern was that many directors appear to be receiving inadequate reporting and training on compliance matters. About a quarter of both CCOs and board members said the compliance function at their organization reports to the board less than once per quarter.
Of training, the report said that in light of a perceived heightened liability exposure for directors, it is puzzling that 44% of director respondents said they hadn’t received any training on compliance issues. Given evolving compliance standards and regulations—such as new Securities and Exchange Commission guidance on conflict minerals and updated DOJ guidance on corporate fraud—it’s arguable that training is more important than ever. Failure to engage in training could amount to a breach of fiduciary duty.
Almost half of respondents, 46%, identified monitoring as the weakest part of their compliance program. Monitoring, however, is particularly important in managing third-party risk, as regulators remain focused on violations related to third parties and as companies struggle to manage sprawling global organizations, DLA Piper said.
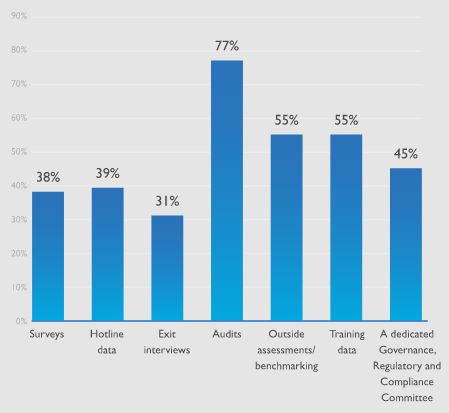
Top tools companies use to rate their compliance program: