In a 6-3 decision this week, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that federal anti-discrimination laws cover LGBTQ+ people and that they cannot be legally fired for their sexual orientation and gender identity, ensuring protection under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Justice Neil Gorsuch wrote in the majority opinion that, “An employer who fires an individual for being homosexual or transgender fires that person for traits or actions it would not have questioned in members of a different sex. Sex plays a necessary and undisguisable role in the decision, exactly what Title VII forbids.”
The decision was based on two separate cases brought before the Court. In 2013, Aimee Stephens was fired from her job as a funeral home director when she revealed her gender identity to her colleagues. Her former boss testified that he had fired Stephens based on the fact that she was “no longer going to represent himself as a man.” The case was the first before the Supreme Court regarding transgender rights. The second case was that of Gerald Bostock and Donald Zarda, who claimed that they were fired from their jobs as a child welfare services coordinator and a skydiving instructor, respectively, for being gay. Both Stephens and Zarda passed away before seeing their cases decided by the Supreme Court.
According to an April 2020 report from UCLA School of Law’s Williams Institute, 8.1 million LGBT workers age 16 and older live in the United States, and before the Court’s ruling, 3.9 million lived in the 28 states where it was legal to fire someone based on their sexual orientation or gender identity. In 2019, the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) brought more than 1,800 charges of LGBT-based workplace sex discrimination. Additionally, a 2017 survey showed that 20% of LGBTQ Americans reported facing discrimination when applying for a job, and 22% were not paid equally or promoted at the same rate as their colleagues who were heterosexual and cisgender. Advocacy organization Out Leadership also reported that, in 2020, “less than 0.3% of Fortune 500 board directors” were openly LGBTQ+.
These factors contribute to workplaces where LGBTQ+ workers do not feel comfortable being themselves, and are more likely to leave, according to Human Rights Campaign (HRC). A 2019 HRC report noted that 46% of LGBTQ+ workers had hidden their sexual preference and/or gender identity at work, and 10% had left jobs because their workplace did not accept LGBTQ+ people.
In the article “The Benefits of Diversity & Inclusion Initiatives,” Risk Management reported that encouraging diversity and inclusion helps all workers and their organizations. Allowing employees to bring their whole selves to the task can be beneficial. As the articled noted, “Often, the outsider believes he or she must bend to the norms of this dominant culture. When this occurs, it mutes creative friction—or creative abrasion, as it is also called—wherein ideas can be challenged productively.” D&I initiatives can encourage employees to more freely innovate and collaborate, can help boost worker retention, and may help minimize the risk of discrimination lawsuits.
But these programs may not be enough to create a working environment that is free of bias and discrimination. Even when companies “fostered an inclusive workplace,” 64% of employees in a 2019 Deloitte survey said that they had experienced or witnessed workplace bias in the past year, and over 50% of LGBT respondents experienced bias at least once a month. Employers can work to address the specific concerns of their LGBT+ workers, including allowing transgender employees to use bathrooms that correspond to their gender identity, regularly updating and reassessing company policies and requiring all employees to review them, and making clear that any form of workplace discrimination is unacceptable and will incur consequences.
Some legal experts worry that workplace discrimination will still take place under the guise of other factors like performance, noting that discrimination based on sexual preference and gender identity is very difficult to prove. The Supreme Court’s decision also left open the possibility that employers could still use a religious exemption to discriminate against LGBTQ+ workers. However, the decision is a critical step forward for LGBTQ+ civil rights and an important moment for workplace diversity and inclusion.

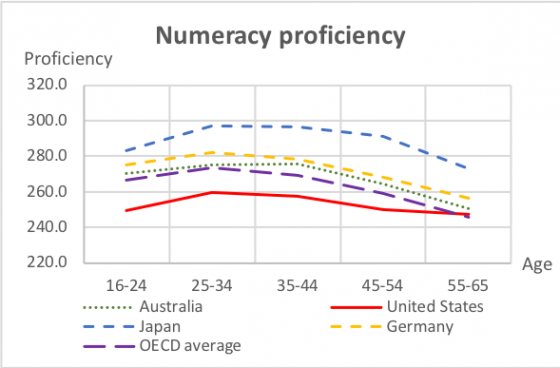
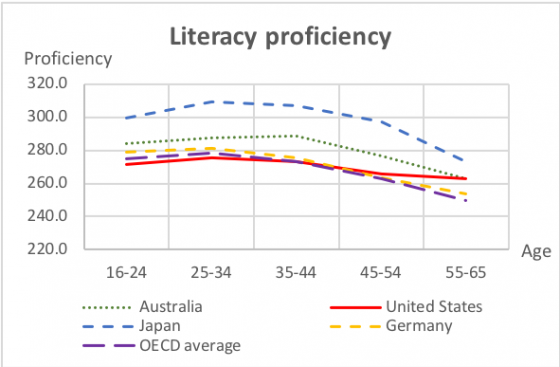
 People are living and working longer today than in the agricultural and industrial ages. The growth in the number and percentage of individuals over 60 and 80 years of age is already having a global impact.
People are living and working longer today than in the agricultural and industrial ages. The growth in the number and percentage of individuals over 60 and 80 years of age is already having a global impact.