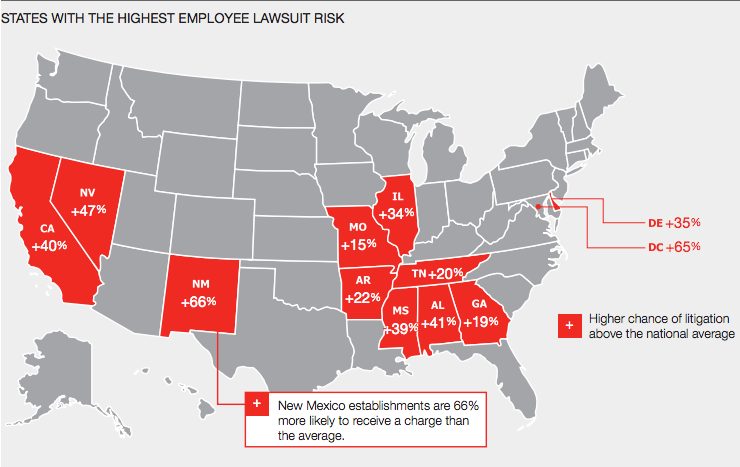
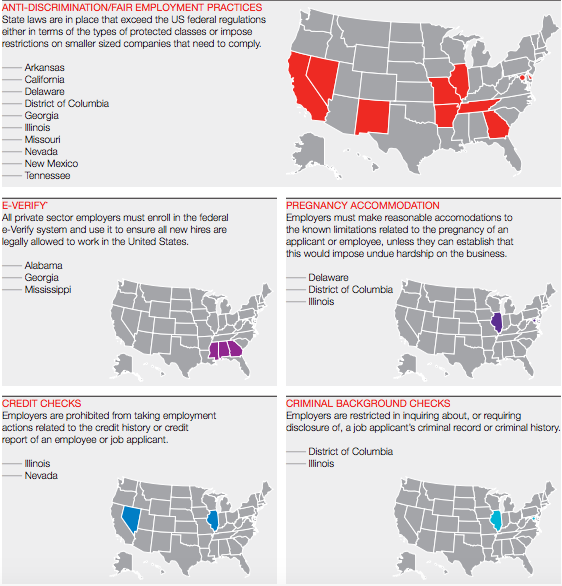
In today’s increasingly litigious society, harassment and discrimination are trending upward. To protect your business from workers’ claims, including wrongful termination, breach of employment contract, wrongful discipline, failure to employ or promote, sexual harassment and discrimination, you likely have employment practices liability insurance (EPLI) in place.
But if your employees frequently deal directly with the public, there may be a glaring gap in your coverage. Your business and workers may also be at risk for harassment or discrimination claims from a customer, client, supplier, vendor or visitor. The bad news: these types of claims are not covered by commercial general liability insurance or standard first-party EPLI.
To protect your business from customer or client allegations, third-party EPLI is the answer.
The types of wrongful acts typically covered by third-party EPLI are discrimination and harassment. Discrimination can include claims based on nationality, sex, disability, age, race, religion, pregnancy or sexual orientation. Harassment can take on many forms, such as unwelcomed sexual advances, requests for sexual favors, and other types of verbal or physical abuse. Third-party EPLI reimburses your company for court and legal fees, as well as any settlements between the business and the accuser.
Third-party EPLI may be appropriate if you frequently meet with clients or deal with vendors. And it is absolutely essential for businesses that interact with the public. Examples include large customer service teams, cable television installers, contractors, restaurant, hotel and transportation workers, and real estate agents.
For example, a customer sued a New Jersey gas station after being sexually assaulted by an attendant who was filling up her car. The woman claimed the station attendant made inappropriate advances, performed a lewd act and touched her while she was buying gas, according to NJ.com. The woman also claimed that another employee at the gas station did nothing to prevent the incident or intervene during it.
In another example that made national headlines, thousands of African American patrons of Denny’s restaurants claimed they were refused service, were forced to wait longer, had to prepay for food, or pay more for food compared to white customers, the New York Times reported. These claims, which totaled 4,300 and spanned several years across multiple states, culminated in a class-action lawsuit against the national restaurant chain. Denny’s settled the suit in federal court, and members of the class-action suit were awarded $54 million for damages.
Starbucks was sued in federal court by a group of 12 deaf customers who said they were mocked and mistreated at a coffee shop in New York City. The group claimed being harassed multiple times because of their disability.
During one instance, a Starbucks employee called the police in response to a group of deaf patrons who met at a Starbucks to hold their monthly Deaf Chat Group, although the patrons were paying customers, according to USA Today. The police apologized to the patrons and reprimanded the employee for calling the police when there was no illegal conduct.
As you can see, the level of interaction a company has with those who might claim a wrongful act, and the industry in which you operate, can affect the cost of third-party EPLI. Other factors come into play as well, like whether you’ve been sued in the past over employment practices.
While third-party EPLI helps defray the cost of lawsuits and judgments brought against your business, one thing it doesn’t protect is your reputation. Therefore, forward-thinking employers are doing more than just purchasing a third-party EPLI policy; they’re also taking steps to make it less likely they will have to use that policy. Effective training and education, no matter your level of exposure, can help prevent claims of wrongful acts against your business or employees. Creating training programs to educate employees on what constitutes harassment and discrimination, as well as putting processes in place about what to do in the event of an allegation, are good starting points.
When screening and hiring new employees, it is essential to create programs that help your hiring team vet candidates solely on their qualification for the job. Documenting your process helps everyone understand the requirements and will provide backup should issues arise.
It’s also a good practice to display all corporate policies as they relate to hiring and worker conduct in employee handbooks so the policy is available to everyone and can be reviewed when necessary. Many companies also ask employees to sign a document affirming they have read the employee handbook.
Unfortunately, all of the education and training in the world can’t stop a customer or vendor from claiming harassment or discrimination by one of your employees. But a carefully developed third-party EPLI plan that assesses your exposure and helps you completely cover your business can minimize your risk.