With the highly-publicized rise in cyberbreaches, we have seen hackers break into systems for a variety of reasons: criminal enterprises simply stealing money, thieves gathering Social Security or credit card numbers to sell on the black market, state-sponsored groups taking confidential information, and malicious actors taking passwords or personal data to use to hit more valuable targets. Now, another group of financially-motivated hackers has emerged with a different agenda that may have even riskier implications for businesses.
According to a new report from computer security company Symantec, a group it calls Morpho has attacked multiple multibillion-dollar companies across an array of industries in pursuit of one thing: intellectual property. While it is not entirely clear what they do with this information, they may aim to sell it to competitors or nation states, the firm reports. “The group may be operating as ‘hackers for hire,’ targeting corporations on request,” Symantec reported. “Alternatively, it may select its own targets and either sell stolen information to the highest bidder or use it for insider trading purposes.”
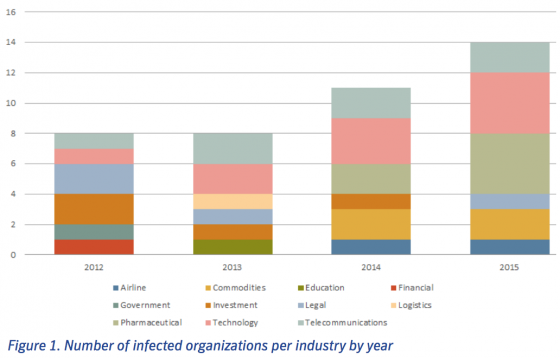
Victimized businesses have spanned the Internet, software, pharmaceutical, legal and commodities fields, and the researchers believe the Morpho group is the same one that breached Facebook, Twitter, Apple and Microsoft in 2013.
Symantec does not believe the group is affiliated with or acting on behalf of any particular country as they have attacked businesses without regard for the nationality of its targets. But, as the New York Times reported, ” the researchers said there were clues that the hackers might be English speakers — their malicious code is written in fluent English — and they named their encryption keys after memes in American pop culture and gaming. Researchers also said the attackers worked during United States working hours, though they conceded that might just be because that is when their targets are most active.”
The researchers have tied Morpho to attacks against 49 different organizations in more than 20 countries, deploying custom hacking tools that are able to break into both Windows and Apple computers, suggesting it has plenty of resources and expertise. The group has been active since at least March 2012, the report said, and their attacks have not only continued to the present day, but have increased in number. “Over time, a picture has emerged of a cybercrime gang systematically targeting large corporations in order to steal confidential data,” Symantec said.
Morpho hackers have also been exceptionally careful, from preliminary reconnaissance to cleaning up evidence.
In some cases, to help best determine the valuable trade secrets they would steal, the group intercepted company emails as well as business databases containing legal and policy documents, financial records, product descriptions and training documents. In one case, they were able to compromise a physical security system that monitors employee and visitor movements in corporate buildings. After getting the data they wanted, they scrubbed their tracks, even making sure the servers they used to orchestrate the attacks were rented using the anonymous digital currency Bitcoin.
In short, the hackers are really good, according to Vikram Thakur, a senior manager of the attack investigations team at Symantec. “Who they are? We don’t know. They are virtually impossible to track,” he said.