 Hurricane Harvey, which made landfall in Texas on Friday night as a Category 4 hurricane, has so far caused at least five deaths and more than a dozen injuries. Now a tropical storm, Harvey has dumped more than 30 inches of rain on the Houston area, with another 15 to 20 inches anticipated by Friday.
Hurricane Harvey, which made landfall in Texas on Friday night as a Category 4 hurricane, has so far caused at least five deaths and more than a dozen injuries. Now a tropical storm, Harvey has dumped more than 30 inches of rain on the Houston area, with another 15 to 20 inches anticipated by Friday.
According to the New York Times:
- With record floodwaters devastating much of southeast Texas, more than 450,000 people are likely to seek federal aid in recovering from Harvey, the storm that has battered the Gulf Coast for days, Brock Long, the director of the Federal Emergency Management Agency, said on Monday. The agency has estimated that about 30,000 people will seek emergency shelter, and that federal aid will be needed for years.
- The Houston region now looks like an inland sea dotted by islands, with floodwaters inundating roads, vehicles, and even bridges and buildings. Thousands of people have been rescued from flooded homes and cars and many more are stuck in homes that remained above water but are cut off.
Bloomberg reports that damage from Harvey is expected to reach as much as $30 billion when factoring in the impact of flooding on the region’s labor force, power grid, transportation and other aspects supporting the energy sector.
Catastrophe modeling firm AIR Worldwide estimates that industry insured losses resulting from Hurricane Harvey’s winds and storm surge in Texas will range from $1.2 billion to $2.3 billion. AIR noted that these estimates do not include the impact of the ongoing torrential rain and catastrophic flooding from the hurricane unprecedented precipitation.
Hurricane Katrina, which struck New Orleans in 2005, caused about $160 billion in total economic damages, with about 47% covered by the insurance industry.
The Wall Street Journal said that despite the high damage anticipated, the timing is good for insurers and their customers:
Personal and commercial insurers have record levels of capital, the money they have on hand that isn’t required to back obligations. With insurers’ overall strong capital position, Harvey is unlikely to cause extensive damage to the industry’s financial strength, although it could hurt quarterly earnings for those carriers with blocks of business in hard-hit areas.
According to the Wall Street Journal, analysts estimate it would take $100 billion or more of losses in a 12-month period to cause distress within the insurance industry. The Insurance Information Institute reported that insurers had $709 billion in surplus during the first quarter of this year, which translates to $1 in surplus for every 75 cents of net premiums.
Although 52% of residential and commercial properties in the Houston metro are at “High” or “Moderate” risk of flooding, they are not in Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHA) identified by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), according to CoreLogic. Properties within SFHA zones, categorized as Extreme or Very High Risk, require flood insurance if the property has a federally insured mortgage. Properties outside SFHA zones are not required to carry flood insurance.
Levels of flood risk for properties in seven metro areas likely to have severe rain and flooding as a result of Hurricane Harvey: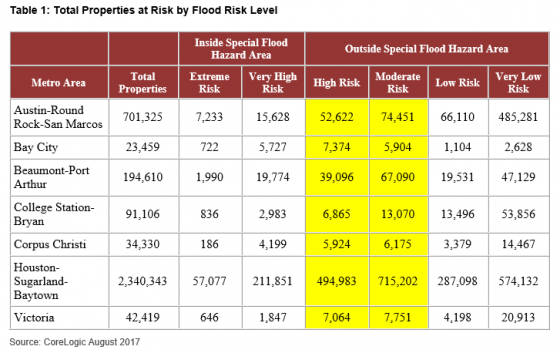
A factor in insurance costs, according to AIR Worldwide, is that more than half of the commercial buildings in both Texas and Louisiana are steel and concrete. Unlike residential structures, commercial buildings are often built to stricter standards, making them less vulnerable than single-family homes. More than 40% of buildings in the U.S. Gulf Coast region meet Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM) standards set in 1980, AIR said.