 Across the vast geography of the United States, flood is no stranger to any of the states. From the March 2018 Nor’Easters that slammed the East Coast to the numerous storms and hurricanes that have swept across the country, both coastal and non-coastal regions are all at risk of flood.
Across the vast geography of the United States, flood is no stranger to any of the states. From the March 2018 Nor’Easters that slammed the East Coast to the numerous storms and hurricanes that have swept across the country, both coastal and non-coastal regions are all at risk of flood.
FEMA reports that 98% of the U.S. counties have been impacted by a flooding event in the past, and 2016 and 2017 are examples of both the frequency and severity that the peril poses. According to Munich Re’s Geo Risks Research, there were more floods in the U.S. in 2016 than any year on record. Hurricane Harvey, the eighth named storm in the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season, caused large flood losses and is reported as the second costliest hurricane in U.S. history after Hurricane Katrina. Major losses from Katrina were caused by flooding due to levee failure.
The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) was enacted by Congress with three main pillars: affordable insurance, floodplain management and flood mapping. Since its inception, the program has helped thousands of home owners with total claims exceeding $65 billion. The NFIP’s role in aiding homeowners was evident during the weeks and months following Hurricane Harvey. According to FEMA, as of January 2018, more than 91,000 NFIP policyholders had filed claims for Hurricane Harvey, and FEMA has paid more than $7.6 billion in losses to those policyholders. the economic losses of Hurricane Harvey, however, are likely to reach $85 billion. Even after considering the commercial insured losses, the gap between the insured and economic losses, known as the “protection gap,” is huge.
Based on events like Hurricane Harvey and Superstorm Sandy it is likely that as many as 80% of the homes in Houston were not insured for flood. In fact, according to the Insurance Information Institute, only about 12% of the home owners in the United States purchase flood insurance; this statistic is even lower in inland states. The number of NFIP policies in the Mississippi River states (which excludes Louisiana) is about 5% of the total NFIP program. Using current building stock data from Homes.com, this would make the purchase rate for flood insurance in the Mississippi states at less than 2%.
Why is there such a large protection gap and why is it important to narrow this gap?
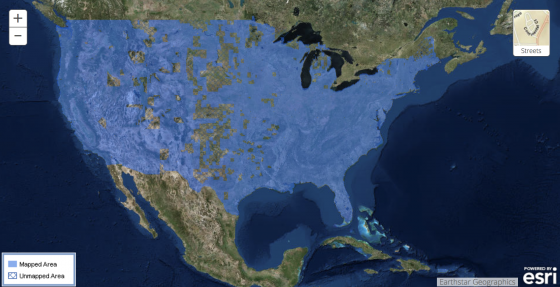
A Floodzonedata.us study by the New York University (NYU) Furman Center found that there are about 6.9 million housing units within the 100-year flood plain as defined by FEMA. According to a February 2018 scientific study in IOPscience, however, “Estimates of present and future flood risk in the conterminous United States,” the actual number of exposed houses could be as high as 15.4 million. In addition, a September 2017 audit by the Department of Homeland Security Office of Inspector General noted that, as of December 2016, only 42% of FEMA’s flood maps are up to date and valid. Both Superstorm Sandy and Hurricane Harvey demonstrated several instances of FEMA maps being inadequate to evaluate the extent of flooding.
Extreme events like Harvey should be viewed as an opportunity for resilience initiatives. Jeffrey Heberg, Chief Resilience Officer for New Orleans, notes that the key to resilience is insurability. In fact, studies highlight the importance of high insurance penetration and the correlation to strong resilient countries.
The stark contrast in the insurance penetration between Chile, Haiti and New Zealand provides an example of the impact the insurance industry can have towards financing the losses from major catastrophes. Following earthquakes in 2010, New Zealand and Chile showed faster recovery due to high insurance penetration and thus the ability to absorb losses, whereas Haiti went through a very slow recovery process due to the lack of catastrophe (re)insurance.
While insurance is an important factor, financial resilience through insurance is not enough. There is a further need for a comprehensive approach to mitigate severe natural catastrophes. This is when public private partnerships (P3s) play a crucial role. In New Zealand, the government-owned earthquake commission, with reinsurance in the global market, resulted in insurance penetration of up to 80%. A similar example of P3 in the United States is the reinsurance protection sought by FEMA to reinsure the NFIP against extreme events.
Public private partnerships rely on the government’s ability to ensure adequate loss prevention, build physically resilient structures and implement forward-looking municipal planning (such as futuristic view of flood maps and flood plain management). If people reside in and build more resilient structures, not only can it help save lives, but the cost of insurance could be less, and the probability of loss and recovery time will be less for communities.
It is not only important to focus on building resilient communities to help protect them from natural catastrophes, it is now becoming a crucial requirement for cities and states. Standard & Poor’s emphasizes the importance of disaster insurance arrangements on sovereign financial resilience. The September 2015 Standard & Poor’s Rating Report notes that a lack of insurance coverage for significant catastrophic events could negatively impact sovereign ratings resulting in a downgrade. As recent as November 2017, Moody’s reported the incorporation of climate change into its credit ratings for state and local bonds. This would mean that communities, cities and states may get downgraded unless they show sufficient adaptation and loss mitigation strategies.
The time for resilience is now. As geographic regions that were once sparsely populated are now filled with burgeoning cities there is so much more at risk from today’s extreme weather events. Insurance can play a role in helping communities recover. Insurance alone, however, is only a partial solution. We also need to build resilient communities to help mitigate the damage caused by flood.


 Across the vast geography of the United States, flood is no stranger to any of the states. From the March 2018 Nor’Easters that slammed the East Coast to the numerous storms and hurricanes that have swept across the country, both coastal and non-coastal regions are all at risk of flood.
Across the vast geography of the United States, flood is no stranger to any of the states. From the March 2018 Nor’Easters that slammed the East Coast to the numerous storms and hurricanes that have swept across the country, both coastal and non-coastal regions are all at risk of flood.