
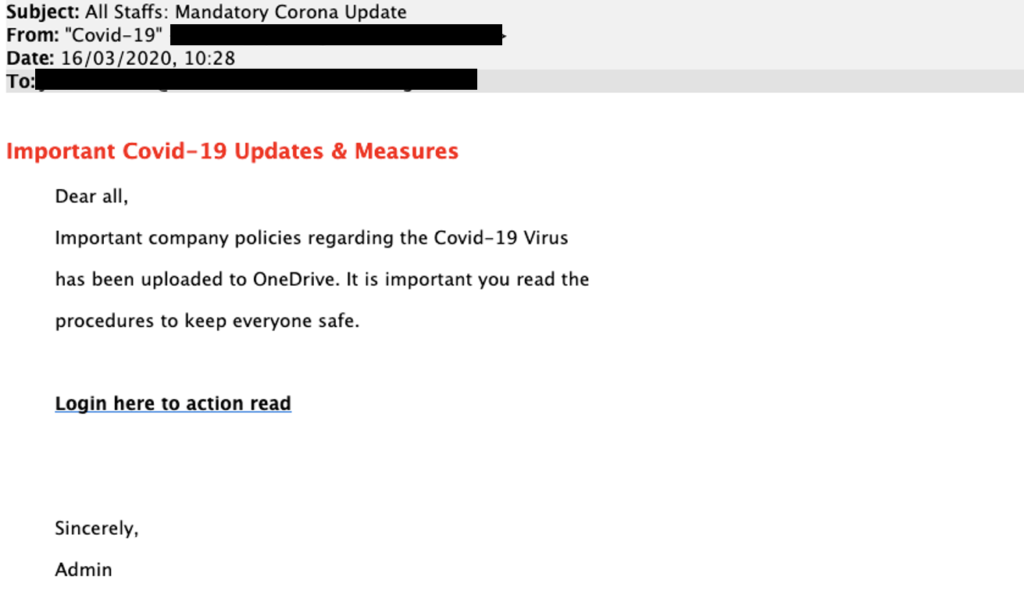
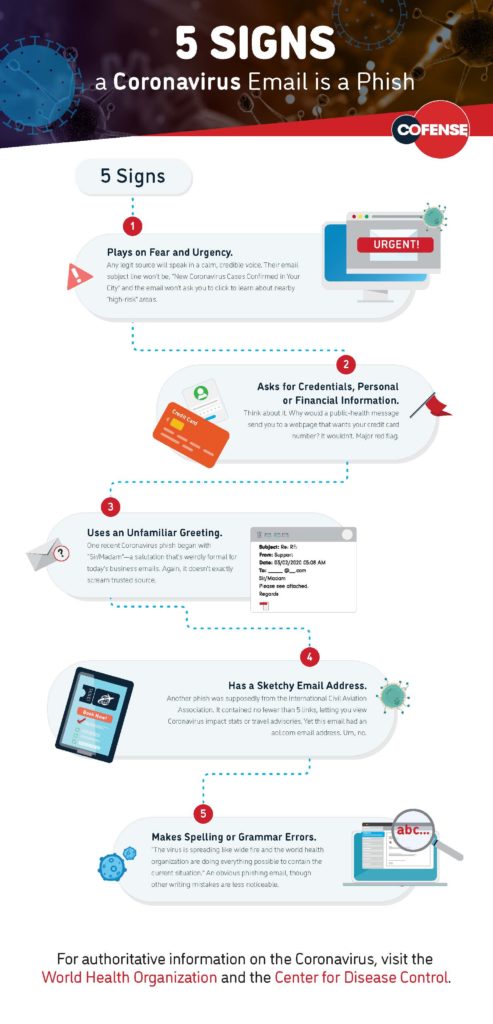
In the first quarter of 2016 alone, more than 40 organizations, including Snapchat, Moneytree and Sprouts Farmers Market, acknowledged they were victims of phishing attacks. The attacks came via emails seemingly sent from CEOs to their own human resources and accounting departments. In reality, these emails were sent by cybercriminals attempting to steal vital personal and financial information from companies and their employees.
The FBI estimates that phishing attacks have cost companies more than $2.3 billion in losses over the past three years, and since January 2015 alone, the agency saw a 270 percent increase in identified victims and exposed losses from CEO scams.
Recipients who “take the bait” by responding to a phishing email often provide scammers with all the necessary information to perpetrate identity theft, including filing a tax return in someone else’s name. Clicking a link or opening an attachment may also launch malware-intrusive software and seriously compromise the system by initiating malicious background programs.
The stakes are high and regardless of your organization’s size, you are always at risk for an attack. In fact, the Anti-Phishing Workgroup discovers more than 40,000 unique phishing sites targeting about 500 brands per month, while the Department of Defense and Pentagon report receiving up to 10 million phishing attacks each day.
The success of attacks varies, with 30% to 60% of incidents resulting in victimization, according to a 2013 Verizon Data Breach Report. A phishing attempt’s success or failure, however, rests beyond a scammer’s ability to infiltrate the cybersecurity infrastructure of an enterprise.
Your organization’s susceptibility really comes down to your people. Even with training, vulnerabilities depend on a combination of employees’ awareness levels and enduring personal habits, according to research by University at Buffalo (UB).
Companies can implement more effective cyber preparedness measures only when they better understand the ways that their employees think and behave. As phishing attacks continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, the most successful employee cyber defense strategies should involve two critical components: 1) a combination of cutting edge training and testing and 2) support programs to alter the unconscious human behaviors that compromise cybersecurity.
Currently, most businesses train employees to recognize phishing attempts by identifying key elements in an email message, such as finding the sender’s address, noticing hyperlinks and recognizing clues like typos or awkward language. But research has shown that those efforts fail to sustain positive results because organizational training focuses on situational reactions while ignoring employees’ existing habits, which are difficult to break.
For example, an employee may successfully identify suspicious emails when prompted in a training session. When it comes to an average Monday morning, however, opening every email to clear their inbox may be a strong habit that training simply does not offset. Phishing is largely successful for this precise reason. Perpetrators take advantage of individuals who are habitual in the way they respond, despite any awareness they may have developed or gained in training, according to UB findings.
Many employers complement this basic training with follow-up penetration testing to evaluate whether employees recognize the warning signs of a cybersecurity threat in practice. Organizations may send a mock email with red flags that indicate a potential phishing attack, such as a compelling subject line like “Your computer is at risk.” Once opened, the recipient sees that the message is from the employer with a warning about how similar future messages could pose risks.
Penetration testing, however, doesn’t work in the long run because it also fails to acknowledge habitual actions and attempts to change a person’s behavior by simply encouraging them to do more of the same behavior.
Organizations can actually address the bad habits by identifying employees who are most susceptible to phishing and exposing them to higher levels of education with an emphasis on creating better tailored interventions that address the underlying “why” that drives people to fall prey to phishing time and again.
Continuously testing employees can be helpful; however, a company’s security training program must also attempt to adjust the daily unconscious behavior of employees that puts networks at risk. Companies need to provide their employees with a relatable (non-security/IT) team member/colleague to demonstrate what responsible cyber behavior looks like day in and day out.
One way to accomplish this is to create an internal cyber ambassador program that identifies employees who have proven themselves to have especially strong cyber awareness.
These employees should be selected from teams such as accounting, sales, HR and administrative support, that are typically vulnerable to phishing attacks.
Cyber ambassadors are responsible for promoting cyber best practices within their own teams. This type of program creates a platooning effect, where employees subconsciously emulate the behavior of their ambassador/team member, resulting in a safer cyber environment.
While employees can be your greatest weakness, they can also be your strongest asset in thwarting phishing attacks. Training employees to identify a phishing attempt—either before or after falling victim to an attack—is only half the battle.
By better understanding the mechanisms behind employee susceptibility, companies can anticipate individuals most at risk, create dynamic security and training policies that promote safe cyber behavior patterns, and alter employees’ habits through colleague support programs.

 The National Cyber Security Alliance (NCSA) announced that its new executive director is Kelvin Coleman, who has held high-level positions in the United States Department of Homeland Security, and the National Security Council.
The National Cyber Security Alliance (NCSA) announced that its new executive director is Kelvin Coleman, who has held high-level positions in the United States Department of Homeland Security, and the National Security Council.