MUMBAI – The inaugural RIMS Risk Forum 2018 India launched on November 13, and leading risk professionals from India and Asia-Pacific countries met for two days to address the challenges facing companies in the region. In a country of 1.3 billion people, expectations are for India’s risk management profession to grow, though some presenters acknowledged the proactive need to fill a potential talent gap.
During the opening keynote address, Dr. Viswanathan Ragunathan, CEO and general manager of the Varalakshmi Foundation said that examining the role of risk in Indians’ behavior and culture will initiate the dialogue among students and aspiring professionals.
“We are obviously a contradiction,” he said. “We are, at once, eternal optimists and fatalistic. At one level you can relate to what I’m saying in that Indians do not take too much risk in their day-to-day lives. Yet anyone who has taken the Mumbai trains knows…it’s almost as if we have a death wish.”
Ragunathan also discussed approaches he tends to use to assess risk, including viewing them in a VUCA environment (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity), where one weighs how much of a situation is known against the results of controllable actions and their predictability.
“The management of volume,” he said, is ultimately at the heart of India’s challenges, and that issue is exacerbated by interconnected risks, such as a dense population and struggling infrastructure. He proposed transparency and broad communication within the Indian risk management community as starting points for solutions.
“The risk manager who understands the risk but does not share it widely does not help,” he said.

As the forum progressed, ISO31000 implementation, natural disasters and resilience, infrastructure, risk frameworks, data storage and diversity hiring practices were some of topics that received special focus on Tuesday.
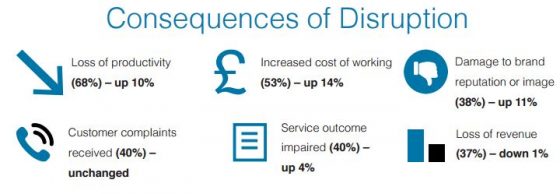
“The State of Risk Management in India” was a Marsh-led panel on the findings from the newly-released, India-wide survey on risk management practices co-conducted by RIMS. The report found that risk managers are a crossroads in India, where they can assume greater leadership roles that transcend just compliance and insurance matters and can expand their knowledge base, hone their skillsets and gain access to best practices, tools and technology.
During “Thinking About Thinking in Risk Management,” Peter Young, PhD of the University of St. Thomas’ Opus, discussed the major questions facing risk managers today. He discussed how, according to his findings, experience rises dealing with uncertainty – as opposed to risk – as one looks further up on the corporate ladder.
“Risk is uncertainty when you have the capacity to measure it, and when you get to the executive suite you hardly ever deal with risk at all because you’re responsible for the strategy,” he said. “I would submit that’s broadly true among organizations at all levels. We are little ships bobbing in a big sea of uncertainty.
“[Executives] can bring a level of comfort operating in an environment of uncertainty. That turned out to be only partly true, but we think it’s an abiding truth that is slowly revealing itself.”
“Diversity in Corporate India” inspired some spirited discussions about how women’s voices and the concept of assumption are emerging as integral parts of hiring practices throughout organizations in India. Panelists were Ragunthian, Praveen Gupta, CEO of Raheja QBE General Insurance Co., and Carissa Hickling, Talent Acquisition Strategy and Technology Global Consultant for Siemens Technology India.

They spoke of how efforts to better represent women have progressed. Additionally, gay and lesbian communities are experiencing a new level of acceptance now since September, when the Supreme Court of India ruled parts of Section 377 – which was introduced in 1864 – was unconstitutional for criminalizing homosexuality. The panel agreed that while talent itself should win above all else, they acknowledged that it was a sign of progress for the nation and should be thought of as such by its corporate sectors. Hickling explained how Indian companies can now use be more open-minded in their hiring and promotion practices.
“When we look at onboarding plans and organizations, these are the moments of truth,” she said. “We can have conversations about making a small change to our HR system because this is an opportunity to change the first impression of our organization.”
She added that Siemens leadership is taking the initiative to recognize same-sex partners when discussing health benefits and taking the progress a step further extending the welcoming to transgender workers. “This is all happening very fast,” she said, “but it is a time when an organization can demonstrate that this is a time when this does matter.”
For more coverage of the forum, visit Risk Management Monitor’s Q&A with Shankar Garigiparthy.
Live RIMScast coverage of the forum is also available. Download Speaking with Leaders in Risk Management Part I and Part II.
And exclusively for RIMS members, download Peter Young’s audio live from Mumbai: Thinking about Thinking in Risk Management: New Skills for the Future.