This morning at the two-day RIMS ERM Conference 2021, attendees got a “sneak preview” of the new RIMS Risk Maturity Model, presented by Carol Fox, former RIMS vice president of strategic initiatives, and Tom Easthope of Microsoft’s enterprise risk management team. RIMS decided to “reboot” the Risk Maturity Model, Fox said, since the original model was launched in 2006, and the field of risk management had changed quite a bit in the years since, as had the world in general.
Easthope outlined how the new Risk Maturity Model was “designed by practitioners, for practitioners” with input from peers, pundits, academics and critics, to show what success looks like in mature organizations. To achieve this, the new model focuses on how advanced an organization’s risk management capabilities are, not necessarily whether the organization had performed specific actions, as the previous model stressed.
Fox told the audience, which attended in person and tuned in online, that the new Risk Maturity Model was built to “grow as the profession grows,” and outlined its five pillars:
- Strategy Alignment: Risk related to strategy can lead to riches or ruin.
- Culture and Accountability: Culture and accountability drive action.
- Risk Management Capabilities: Risk management capabilities encompass more than proficiencies in a single process.
- Risk Governance: Integrated governance leads to performance improvements.
- Analytics: Analytics are the engines to inform decision making and influence action.
The model is also customizable for each individual organization’s goals and context. When answering the model’s questions, risk managers will have the opportunity to specify their organization’s target on each metric. Success is then measured along five tiers, with Tier 1 being “No formal capacity in place” and Tier 5 indicating that “Capability exists in a continuous improving cycle, informed by internal/external inputs.” The model will not only give a score, but also provide risk managers next steps to help them advance their programs to the next level.
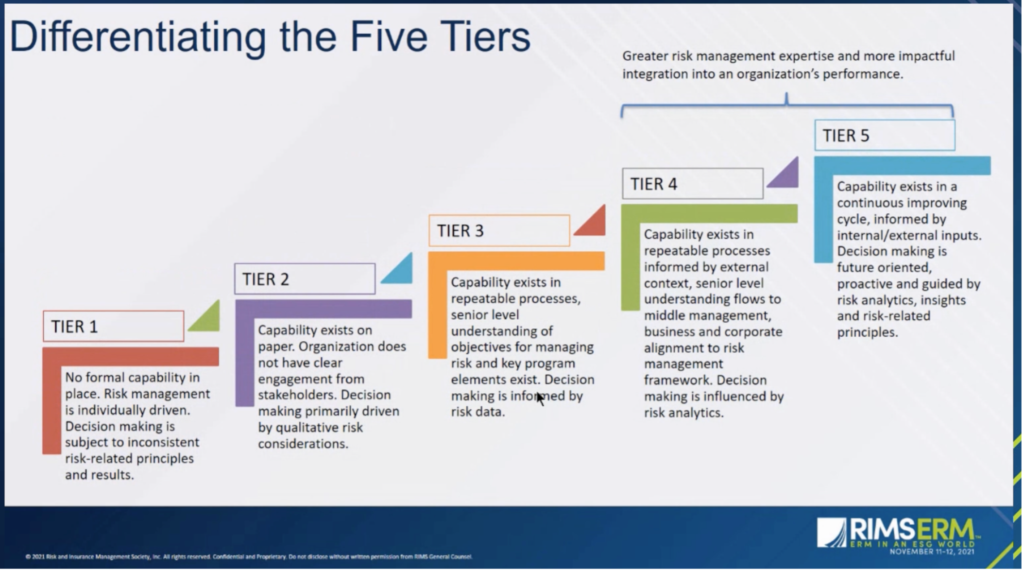
As more people enter data and use the model, risk managers will be able to compare their own performance against that of other organizations and industries—though the presenters stressed that the data provided will be anonymized to both users and the researchers behind the scenes. Companies will also be able to access reports on different respondents across departments to see how answers differed within the organization.
The presenters extended an invitation to participate in the next phase of testing and to give feedback. The goal, they said, is for the model to reflect the reality of risk management today and to “evolve with the world that we live in.” Beta testing is slated to begin in December and to get involved, interested risk managers can contact the organization through the RIMS app, get in touch with Fox and Easthope via LinkedIn, or email RIMS vice president of strategic initiatives Soraya Wright.
This session and many others from the conference can be viewed on-demand online after the event.

 always the case.
always the case.
