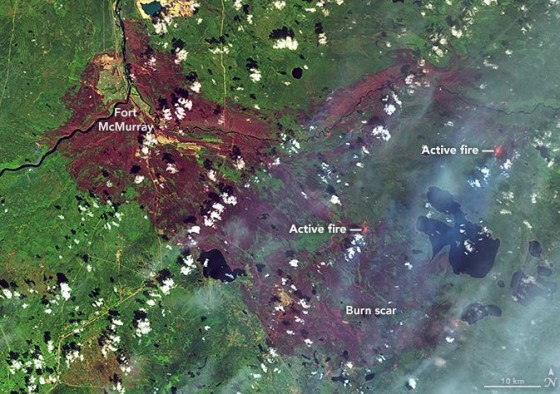
Wildfire season has started two months early in Canada, and the devastating scale of the blazes is already unprecedented. Over 400 fires have caused roughly 10 million acres of burn damage so far, and have blanketed a wide swath of North America in smoke, creating orange skies and toxic levels of air pollution for communities all the way from Canada to the Southeastern United States. During the first week of June, New York had the worst air quality on Earth, and the air quality reached hazardous levels in Philadelphia and Washington, D.C. While it has begun to clear in the Northeast, the fires are ongoing and the air quality may continue to change in the days and weeks to come.
Find more answers to common questions about the wildfires below:
Where is all the smoke coming from?
Unfortunately, there is not just one answer for that, as there are multiple regional fires breaking out seemingly all over Canada and even the United States. However, the current air quality issues are coming from out-of-control wildfires in Quebec and Ottawa, Canada. There are also wildfires breaking out in at least six U.S. states, including Missouri, Kansas and New Mexico, but these do not appear to be involved in the air quality crisis.
According to the Associated Press and Canadian officials, the fires in Canada mark the start of what is expected to be Canada’s worst wildfire season ever due to drier ground than usual, which led the fires to accelerate very quickly.
“Right now, with the manpower we have, we can fight about 40 fires at the same time,” said Francois Legault, premier of Quebec, in an interview with Reuters. “But we have 150 fires, so we have to make sure that we focus where the problems are more urgent.”
In total, there are 425 active fires throughout Canada, according to Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre, and 232 are considered out of control. About 120,000 Canadians have been displaced from their homes due to emergency evacuations, with the most recent being from remote parts of Northern Quebec, according to Reuters. There are fires in nearly all of Canada’s provinces. The current wildfires in the U.S. have led to no evacuations thus far.
Why is the U.S. experiencing poor air quality?
To put it simply, the Northeastern region of the U.S. and the rest of the Eastern seaboard as far down as South Carolina are stuck in a slow-moving weather pattern that is carrying the smoke and smell from the Canadian fires southward. According to Politico, 13 U.S. states are under air quality alerts, impacting over 55 million people.
The AP noted that smoke from various Canadian fires has actually been showing up in parts of the U.S. since May, but with new fires recently breaking out in Quebec, the air quality has increasingly gotten worse in both Canada and the U.S. The hazy, orange-tinted skies and smoke smell along the eastern U.S. are expected to dissipate soon but may still be present through the weekend.
How do the fires impact businesses?
The fires affect certain industries more than others. Outdoor work like construction, sporting events, primary schools, park services and zoos are continuing to pay close attention to the air quality and have suspended outdoor operations accordingly while air quality is at such dangerous levels. Many professional sporting events have been cancelled. The New York Yankees, Chicago White Sox, Philadelphia Phillies and Detroit Tigers have postponed baseball games throughout the week, with minor league baseball teams, soccer teams and WNBA teams following their lead.
During the course of the week, airports have been taking various precautions, with JFK, LaGuardia and Newark Liberty International Airport grounding flights, shutting down inbound flights and changing flight schedules. Similar precautions were taken at Philadelphia International Airport. Because this is an ongoing situation, these measures and flight operations remain in flux.
How do we manage the risk?
In terms of immediate action, experts recommend staying indoors, wearing a mask if going outside and keeping windows and doors closed until the air quality alerts are lifted. By the end of the week, New York City’s air quality is expected to be upgraded from “unhealthy” to “unhealthy for sensitive groups.” To find out about your specific area, visit AirNow.gov.
Looking longer-term, the current fires are a good reminder that natural disasters stretch far beyond hurricanes, flooding and tornadoes, especially as the climate continues to change. A recent study found that increases in burned forest area across the western U.S. and southwestern Canada over the last several decades can be linked to significant human-caused climate change.
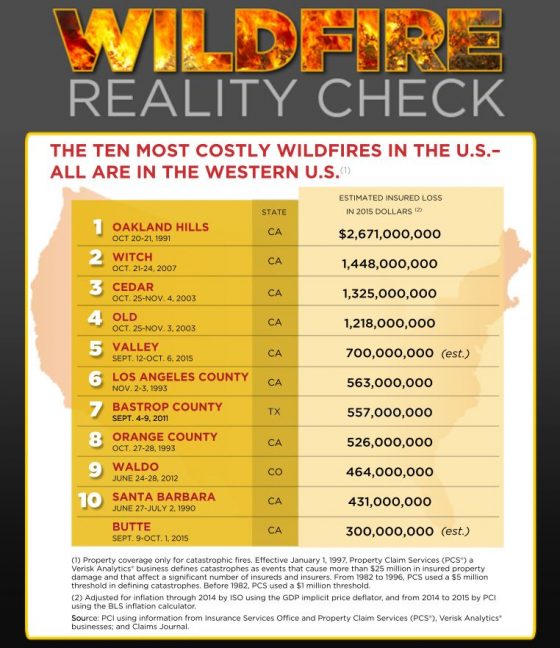
For businesses, take this as a reminder to examine how your organization will handle fallout from wildfires, for example, reviewing your property insurance, business interruption coverage, disaster recovery plans or emergency communications procedures. The following resources from Risk Management can help organizations consider the many risks wildfires and other climate change-related extreme weather events pose to businesses and communities, and can help boost disaster preparedness for these devastating events.
More resources:

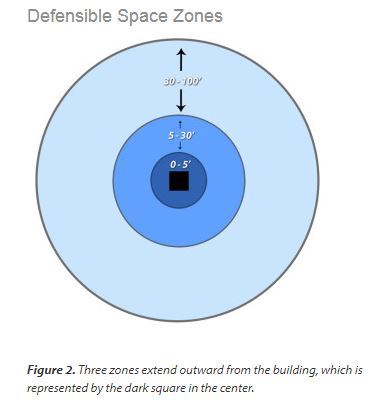 the risk of fire. This includes consideration of specific types of plants and how they are grouped and maintained.
the risk of fire. This includes consideration of specific types of plants and how they are grouped and maintained.
 stems; they may have flooding from sprinklers, which, mixed with soot, can cause other complications; there may be smoke damage, which can by carried throughout a building through air conditioning systems; and there can be chemical residue from fire suppression systems.
stems; they may have flooding from sprinklers, which, mixed with soot, can cause other complications; there may be smoke damage, which can by carried throughout a building through air conditioning systems; and there can be chemical residue from fire suppression systems.