Just as Santa Claus brings gifts down chimneys, his name alone also carries the stigma of risks that transcend all industries. Indeed, thanks to the logistics of his job we better understand the risks of reindeer-led aviation. But perhaps more importantly, Kris Kringle’s presence has long influenced finance and business.
Just as Santa Claus brings gifts down chimneys, his name alone also carries the stigma of risks that transcend all industries. Indeed, thanks to the logistics of his job we better understand the risks of reindeer-led aviation. But perhaps more importantly, Kris Kringle’s presence has long influenced finance and business.
Mentioning him on Wall Street this year may trigger an underlying wealth management risk. The annual “Santa Claus Rally” marks an uptick in the stock market and a 1.4% average return of the S&P 500 index from the last five trading days of the year through the first two of January. This phenomenon can be attributable to people spending and investing a bit extra – possibly from holiday bonuses – leading to a generally happy mood on and off trading room floors.
Since 1950, the market has declined only 15 times during the Santa Claus Rally period. But due to the uncertainty surrounding the tax reform plan making its way through Congress, that 1-in-4.4 chance of downturn is on the minds of cynical investors. As reported recently by Investopedia, “Some bears think that, if Congress fails to make appreciable progress on tax reform before their holiday recess, Scrooge or Krampus will elbow Santa aside, and send the markets downward at year-end.”
And similar to the way Punxatawney Phil seeing his shadow on Groundhog Day can predict six more weeks of winter, Santa skipping stock exchanges’ chimneys may indicate a frosty new year. According to The Stock Trader’s Almanac, some of the more recent holiday seasons without a rally included the last two, as well as in late 2007 and early 2008 leading up to the financial crisis, and just before the dotcom bubble burst in the 1999-2000 holiday period.
Santa’s influence isn’t just relegated to stock speculation and short-term investments, however. Some executives and employees may emulate his work ethic without realizing it. All eyes turn to him in good times and especially during the bad. He’s trying to meet year-end quotas while keeping a workforce happy and focused. Plus, Santa has the burden of trans-meridian travel with frequent stops over a 24-hour period, which is sure to cause jet lag. Sound familiar?
While one all-nighter might not have major long-term effects, regular ones could lead to shift work disorder, which has been linked to chronic diseases and illnesses. Anyone known to “Santa Claus it” too frequently may accumulate a large “sleep debt” over time. According to the Sleep Foundation, “if you work at night, you’re also going against your biological clock, which is naturally cueing you to become less alert and encouraging you to sleep during the nighttime hours.”
This can lead to seasonal “presenteeism,” an issue Risk Management magazine recently explored, detailing pain management in the workforce. Presenteeism occurs when a worker inhabits a space at their job, but “is unable to focus and perform as expected” and can be an even greater drag on productivity than absenteeism. The condition is indiscriminate – it can affect interns and CEOs – and may cause someone to “miss out not only on the income, but also the sense of meaning, purposefulness and belonging that can be gained from a job. Initial distress may lead to chronic anxiety and even depression.”
Identify these risks now, so that the mention of Santa Claus doesn’t put a humbug in your eggnog this holiday season.

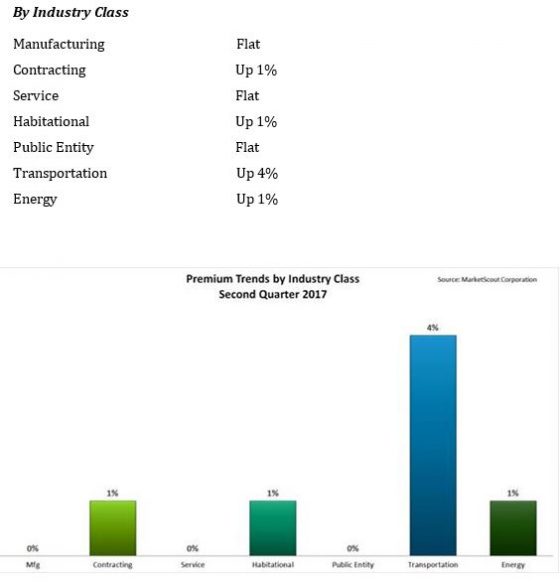
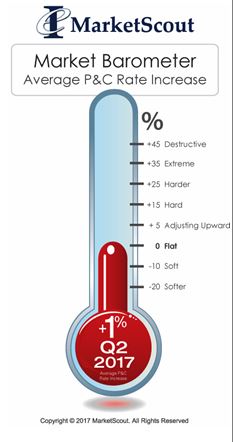 transportation sector, most notably auto-related exposures, is seeing the highest increases, up to 4%, according to a report released today by MarketScout.
transportation sector, most notably auto-related exposures, is seeing the highest increases, up to 4%, according to a report released today by MarketScout. By coverage class, commercial property and inland marine adjusted from down 1% in the first quarter, to up 1% in the second quarter. Commercial auto rates rose from up 3% to up 4%. EPLI also went from up 1% to up 2%. Fiduciary adjusted downward to flat or no increase compared to up 1% in the prior quarter. All other coverage classifications were unchanged from the previous quarter, according to the report.
By coverage class, commercial property and inland marine adjusted from down 1% in the first quarter, to up 1% in the second quarter. Commercial auto rates rose from up 3% to up 4%. EPLI also went from up 1% to up 2%. Fiduciary adjusted downward to flat or no increase compared to up 1% in the prior quarter. All other coverage classifications were unchanged from the previous quarter, according to the report.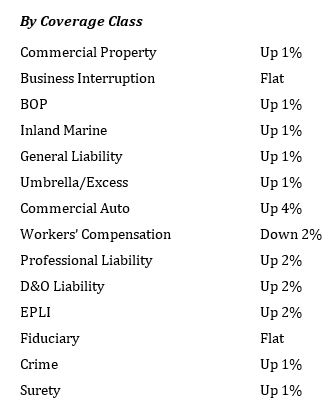 By industry class, public entity rates moderated from up 1% to flat.
By industry class, public entity rates moderated from up 1% to flat.