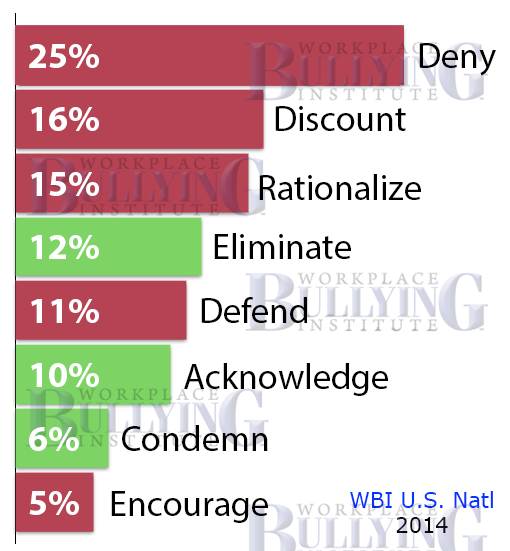
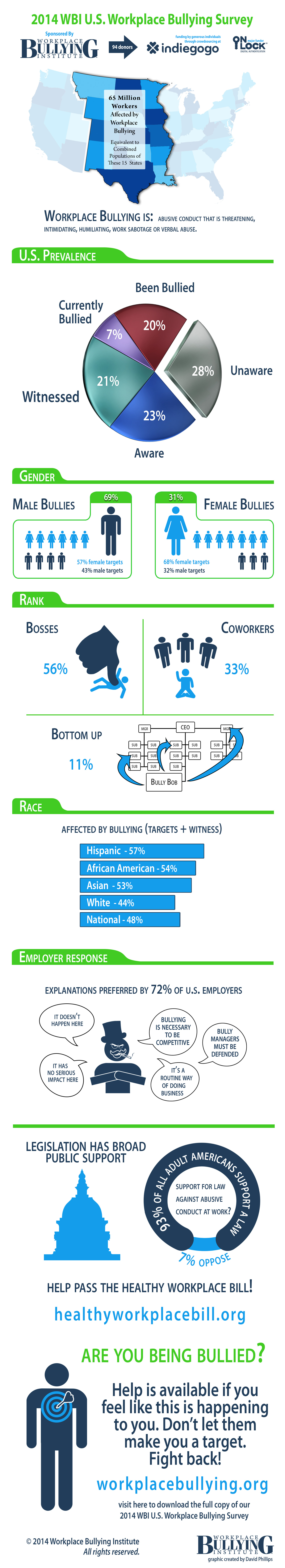
Since its passage in 2010, the Affordable Care Act (ACA), commonly referred to as health care reform, has been the subject of intense political debate and a source of anxiety for many employers. Although most employers have focused on the law’s health benefit requirements, the ACA is also expected to impact how they manage their workers compensation costs in the following ways:
Workers’ Health
Proponents of the ACA say that it will lead to a healthier society. Advocates say that because more people will have access to health care, there will be a reduction in comorbidities. There is, however, no significant evidence to support this contention. For example, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate that heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the United States and that the percentage of Americans with a high body mass index has steadily climbed over the last 50 years—two trends that are not confined to the uninsured population.
Cost Shifting
Employers have long been concerned that injuries from non-work-related causes will be shifted to workers compensation. Doing so is tempting because of workers compensation’s combination of higher reimbursement rates for medical providers and lack of deductibles and co-payments for employees. Some have speculated that the greater access to health insurance promised by the ACA will reduce this shift to workers comp.
It has become clear, however, that the law will not result in all Americans having health insurance coverage. With the ACA requiring that employers offer coverage to all employees working 30 or more hours per week starting in 2015, one-in-10 large companies are planning to cut back on hours for at least a portion of their workforce, according to “Mercer’s National Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Plans” 2013.
Access to Care
Probably the most predictable outcome of the ACA is that it will increase the number of individuals in the U.S. with health insurance coverage. Despite the potential benefits, this could put additional stress on a health care system that is already short on doctors.
This is particularly troubling as it relates to specialists and the potential for delays in obtaining diagnostic tests and scheduling elective surgeries and other procedures. Longer periods of disability and complications as a result of such delays would ultimately drive workers’ compensation costs up.
With this added pressure on a limited number of medical providers, it becomes more important than ever for employers to develop medical networks that focus on quality of care and outcomes—even if it means paying more on a fee-for-service basis.
Standards of Care
Traditionally, the health care industry’s focus has been on volume; more patient admissions, tests, and procedures translated to higher revenues. Post-reform, however, the industry has shifted its focus to improving standards of care and achieving better patient outcomes.
If this transition results in less emphasis on costly procedures, which often produce questionable results, workers’ compensation costs could be reduced.
Although it remains to be seen whether the standards of care developed under the ACA for group health care would be enforced under workers compensation, this is a promising development for employers.