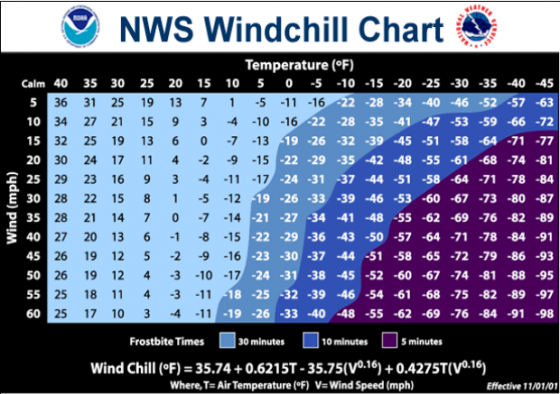
During this winter’s extreme cold spells, caused by a polar vortex creating frigid temperatures, workers are at added risk of cold stress. Increased wind speeds can cause air temperature to feel even colder. This increases the risk of cold stress for those working outdoors—including snow cleanup crews, construction workers, postal workers, police officers, recreational workers, firefighters, miners, baggage handlers, landscapers and support workers for the oil and gas industry.
The U.S. Department of Labor notes that what constitutes extreme cold and its effects can vary across the country. In regions that are not used to winter weather, for example, near freezing temperatures are considered “extreme cold.” Because a cold environment forces the body to work harder to maintain its temperature, as temperatures drop below normal and wind speeds increase, heat can leave the body more rapidly.
Wind chill is the temperature felt by the body when air temperature and wind speed are combined. For example, when the air temperature is 40°F, and the wind speed is 35 mph, the effect on exposed skin like an air temperature of 28°F.
Cold stress can occur when the skin temperature goes down and the internal body temperature (core temperature) drops. This can lead to serious health problems and also cause tissue damage and possibly death. Exposed workers are vulnerable to hypothermia, frostbite and trench foot, the DOL said.
Some risk factors that contribute to cold stress are:
- Wetness and dampness, dressing improperly and exhaustion
- Predisposing health conditions such as hypertension, hypothyroidism and diabetes
- Poor physical conditioning
The DOL recommends that employees working in frigid temperatures avoid alcohol, smoking and some medications to help minimize risks.
The best way to avoid cold stress is by wearing proper clothing. The type of fabric makes a difference as well. For example, cotton loses its insulation value when it becomes wet, while wool, silk and most synthetics retain their insulation even when wet.
Here are some clothing tips for workers in cold environments:
• For better insulation wear at least three layers of clothing: An inner layer of wool, silk or synthetic to wick moisture away from the body; a middle layer of wool or synthetic to provide insulation even when wet; and an outer wind and rain protection layer that allows some ventilation to prevent overheating. Avoid tight fitting clothing.
• Wear a hat or hood to help keep the entire body warm.
Hats reduce the amount of body heat that escapes from the head.
• Wear insulated boots or other appropriate footwear.
• Keep extra clothing (including underwear) handy in case clothing gets wet.
• Do not underestimate the wetting effects of perspiration. Venting of the body’s sweat and heat can be more important than protection from rain or snow, according to the DOL.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also issues guidelines. For example, because it is easy to become dehydrated in cold weather, employers can provide warm sweetened liquids to workers. Additionally:
• If possible, schedule heavy work for the warmer part of the day. Assign workers to tasks in pairs so that they can monitor each other for signs of cold stress.
• Allow workers to interrupt their work if they are extremely uncomfortable.
• Give workers frequent breaks in warm areas.
• Acclimatize new workers and those returning after time away from work by gradually increasing their workload. Also allow more frequent breaks in warm areas to help them build tolerance for working in the cold environment.
These and other safety measures should be incorporated into the organization’s health and safety plan.