For the most part, a company never anticipates its suppliers will be using child labor to provide a product, but for many large corporations with production facilities or suppliers in poorer countries, that is exactly what is, and has been, happening. And the reputation damage inflicted by accusations that a company uses child labor to make a profit, even if unaware, is devastating.
You may remember back in 2007 when Gap came under fire for, apparently unknowingly, using child labor in the production of a line of children’s clothing in India. An investigative reporter videotaped the scene at the factory.
It shows children who appeared to be between the ages of 10 and 13, stitching embroidered shirts in a crowded, dimly lit work-room. The video clearly shows a Gap label on the back of each garment. The reporter, Dan McDougall, said the children were working without pay as virtual slaves in filthy conditions, with a single, backed-up latrine and bowls of rice covered with flies. They slept on the roof, he said.
Though Gap immediately ordered a full evaluation and had a clean record of ethical out-sourcing up until that point, the reputation damage was severe and lingers to this day.
But Gap is not the only company accused of using child labor. In 1998 Nike agreed to root out underage workers and require overseas suppliers to meet strict Unites States health and safety standards after it received heavy pressure from critics.
Nike said it would raise the minimum age for hiring new workers at shoe factories to 18 and the minimum for new workers at other plants to 16, in countries where it is common for 14-year-olds to hold such jobs. It will not require the dismissal of underage workers already in place.
Though the shoe and apparel giant took some steps to ease the concerns of critics, the company suffered boycotts by consumers who refused to support such “sweatshops.” Examples include this boycott petition and this website encouraging the end of support for anything Nike.
More recently, Apple “said it found more than a dozen serious violations of labor laws at its suppliers.” One investigation found that three overseas facilities had hired 11 workers who were 15 years old (the minimum employment age is 16 in those countries). Apple’s reputation damage continued to worsen this year with news of an alarming rate of suicides at its biggest supplier, China’s Foxconn (check out an in-depth article on the topic).
China, India, Bangladesh, Nigeria and Pakistan are among the countries with the most widespread abuses of child workers, according to a report released today by Maplecroft. Below is a map illustrating the ares most prone to use of child labor.
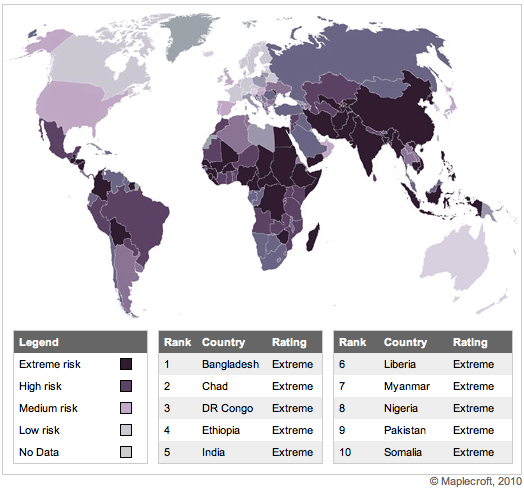 As the report states, there are more than 200 million children working throughout the world, many full-time. Of these, 126 million are exposed to hazardous forms of child labor. As we have seen, many big-name companies have been accused of using child labor, and though they’ve taken many steps to correct their ethical violations, the reputation damage still lingers — and may do so forever.
As the report states, there are more than 200 million children working throughout the world, many full-time. Of these, 126 million are exposed to hazardous forms of child labor. As we have seen, many big-name companies have been accused of using child labor, and though they’ve taken many steps to correct their ethical violations, the reputation damage still lingers — and may do so forever.

