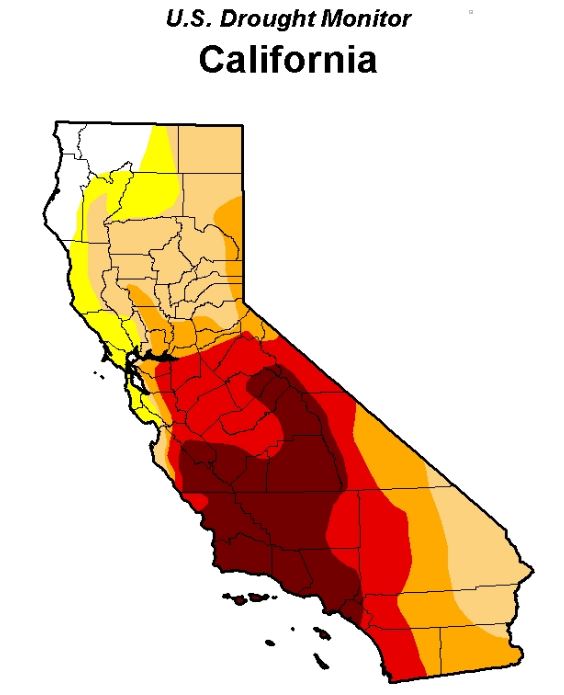
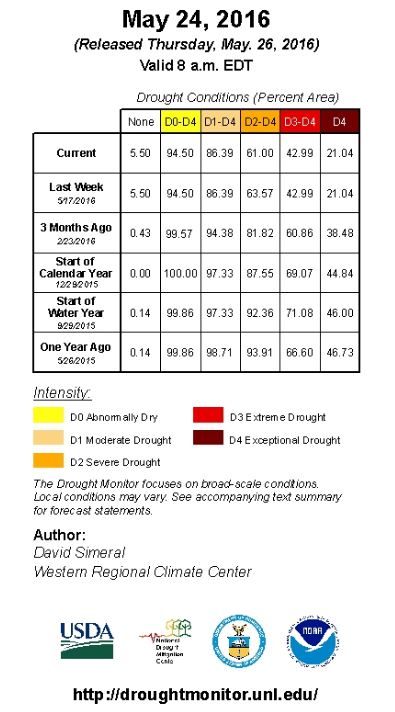
With higher levels of rain and snowfall over the winter, California’s water situation has eased in some areas, prompting the state to initiate new water conservation rules, adopted on May 18 and in effect June 1 through January 2017. The regulations give control over water usage to local communities, which means more restrictions in some areas than in others. In Northern California, winter precipitation has filled some reservoirs, while drought conditions persist in Southern California.
The previous rule—enacted in April 2015 by Gov. Jerry Brown, who issued an Executive Order mandating a 25% reduction of urban water usage from 2013 levels over a nine-month period—saw a savings of about 424 billion gallons. That followed a failed year-long effort to achieve a voluntary 20% reduction in water usage, with statewide conservation results averaging between just 7% and 12%.
The State Water Resources Control Board explained that the new approach replaces the percentage reduction-based water conservation standard with a localized approach. The emergency regulation requires that urban water suppliers ensure that at least a three year supply of water would be available to their customers in case of drought conditions. Suppliers that would face shortages under three additional dry years are now required to meet a conservation standard equal to the amount of a shortage. A water agency that projects it would have a 10% supply shortfall, for example, would have a mandatory conservation standard of 10%. The regulation also makes previously passed water-wasting rules permanent, including no hosing of sidewalks, washing cars without a hose nozzle, or watering lawns within 48 hours of measurable rainfall.
“El Nino didn’t save us, but this winter gave us some relief,” Water Board Chair Felicia Marcus said in a statement. “It’s a reprieve though, not a hall pass, for much if not all of California. We need to keep conserving, and work on more efficient practices, like keeping lawns on a water diet or transitioning away from them. We don’t want to cry wolf, but we can’t put our heads in the sand either.”
Will Sarni, director and practice leader of water strategy at Deloitte, agrees with the direction the state is taking on conservation.
While it may appear that restrictions are being eased, which could send the message that things are going back to business as usual, “It’s not business as usual, but local entities are being given more control,” Sarni said. “My view is that water is ultimately a local issue, so providing greater flexibility and decision-making at the local level that aligns with an overall strategy within the state, or nation, makes sense.”
The model of local management actions that roll up to a regional entity have successfully been adopted in other parts of the country, he said, explaining that states do work together. One example is the Delaware River Basin Commission, which is an entity that has a say in how water is managed in the Delaware River. Other examples include the Great Lakes Commission and the Colorado River Compact. “So cooperating on water is actually more common than not,” Sarni said.