A spate of recent cases offers a clear warning for the food industry about the legal and reputational perils of not getting more serious about supply chain control.
On Monday, the U.S. Supreme Court declined to consider an appeal from Nestle, Archer Daniel Midlands Co. and Cargill Inc., allowing a slave and child labor lawsuit to proceed against the three food industry giants.
Three plaintiffs who claim they were trafficked from Mali as child slaves and forced to work harvesting and cultivating beans in Cote d’Ivoire, and allege that the companies aided, abetted or failed to prevent the torture, forced labor and arbitrary detention they suffered.
According to Reuters:
The plaintiffs, who were originally from Mali, contend the companies aided and abetted human rights violations through their active involvement in purchasing cocoa from Ivory Coast. While aware of the child slavery problem, the companies offered financial and technical assistance to local farmers in a bid to guarantee the cheapest source of cocoa, the plaintiffs said.
The defendants knew about the child slavery problems in the region and offered both financial and technical farming assistance to support the agriculture methods in place, the plaintiffs claim. What’s more, they say, the defendants could have used their leverage in the cocoa market to stop or limit the alleged child labor practices and failed to do so.
According to the Wall Street Journal:
Mark Theodore, a partner at Proskauer Rose, said that the ruling reinforces to companies that they need to be socially responsible employers. And while there is no way to ever completely prevent such risks, he said the ruling is a reminder to companies that they “should be monitoring and also maybe doing a little bit of introspective thinking about their own practices to avoid these things, or prevent them from happening, or to put themselves in legally defensible position if they can’t prevent them.”
In September, the Justice Department finalized a landmark conviction of the former head of the Peanut Corporation of America, who was sentenced to 28 years in prison for knowingly shipping salmonella-tainted products that sickened 714 people and killed nine. That may be the department’s first step in a new approach to taking food industry product safety more seriously, and more aggressively pursuing wrongdoing on a criminal level. The Justice Department has now opened formal investigations into the e. coli outbreak at Chipotle and the listeria outbreak at Blue Bell Creameries, both of which sickened hundreds of consumers.
The department has already signaled a broad intention to focus more efforts on individual law-breakers in corporate crimes. Now, the government appears to be showing the food industry that things are changing in terms of corporate responsibility and food safety, according to Andrew Lankler, partner at Baker Botts. Lankler told the Wall Street Journal that the Department of Justice is signaling that whatever standard the food industry thought it needed to meet for food safety, the bar is higher. “The department is going to step up enforcement in areas where they can prove they sold tainted product,” he said.
And the trouble at Chipotle shows little sign of abating. The CDC is still investigating multiple outbreaks, and the chain has now been served a subpoena as part of a criminal probe by the U.S. Attorney’s Office and the Food and Drug Administration’s Office of Criminal Investigations regarding an isolated norovirus incident in August.
A fourth lawsuit was recently filed by a customer who claims he was sickened by the same strain of e. coli linked to Chipotle, but this case dates back to July, meaning far more people may have been affected in the outbreaks. At least nine suits have been filed by customers, and Bill Marler, a food and safety litigator in Seattle, claims more are coming from the 75 Chipotle-related clients he represents.
At this week’s ICR conference this week, CEO Steve Ells said he is hopeful that the CDC will soon declare the restaurant’s e. coli outbreak over, adding, “we know that Chipotle is as safe as it’s ever been before.”
To that end, Chipotle announced today that it will close all of its stores on Feb. 8 to have a corporation-wide meeting with all staff regarding food safety.
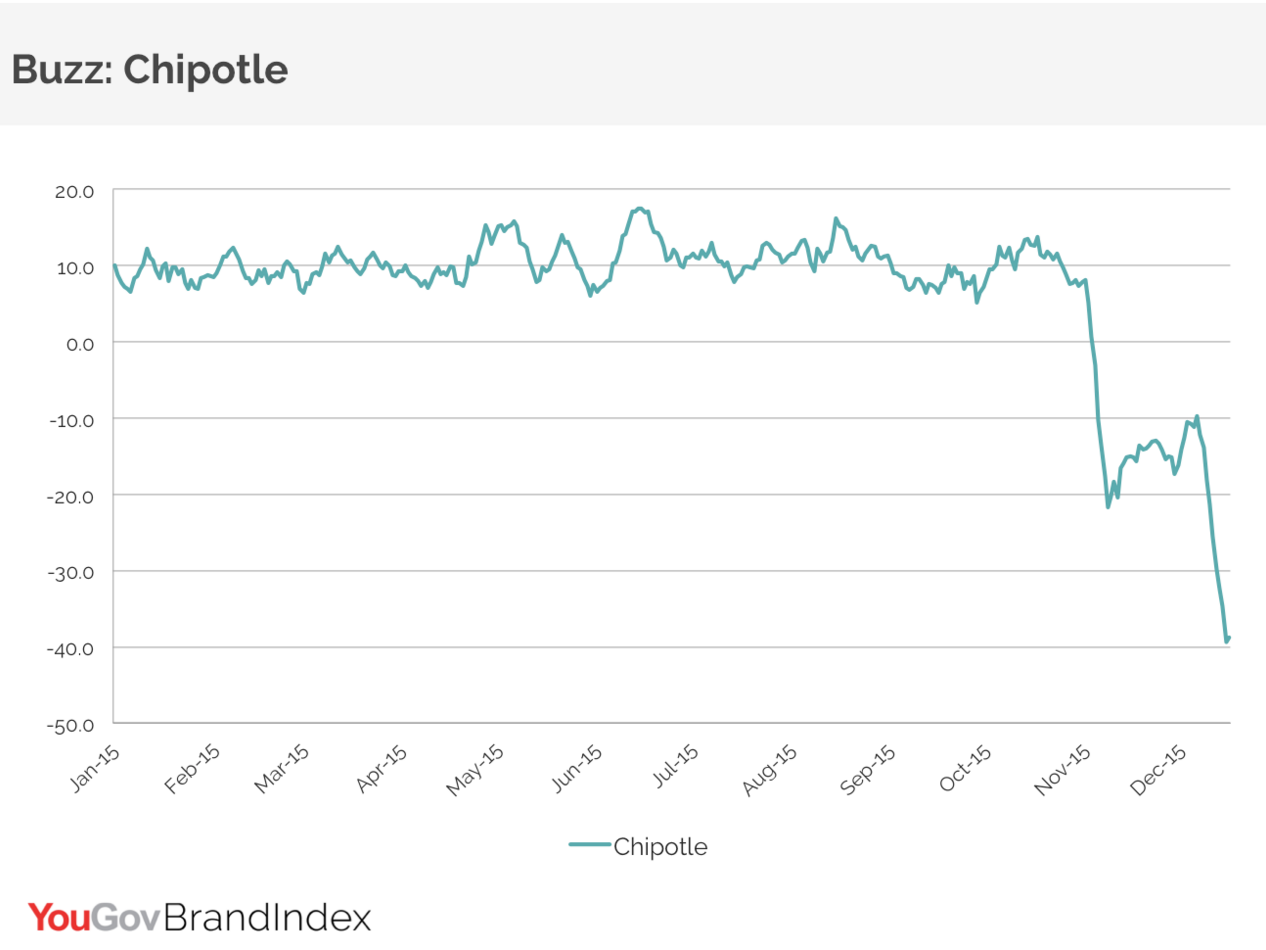
But customers remain extremely wary. Indeed, while it may be an e. coli cliché, it would not at all be a stretch to say public opinion about the brand remains in the toilet, with YouGov’s BrandIndex score for the company seeing a drop equal to that of GM during its crisis.
To combat that, the company also announced plans to launch a sizable new marketing campaign to win back customers, using direct mail and traditional advertising to attempt to win back consumer confidence. As Fortune reported, executives said the campaign will attempt to provide a “detailed story of what happened” to explain to customers why they are now safe, and that it will not focus overtly on food safety, but will have “an undertone” of humility.
Chipotle’s stock dropped nearly 42% in the wake of the outbreaks, and according to an SEC filing, sales at stores open more than a year were down 30% last month. Ells and his team admitted they could not guess how much the fallout will impact 2016 financial results, but expect it will be a “messy” year. Costs are expected to go up from the marketing campaign and new food safety measures, including processing more food through centralized kitchens in an attempt to better control the conditions of ingredients.
The company darkened its outlook for Q4 results, and As Wells Fargo Securities wrote in a recent research note, “We expect CMG to point to a hard-fought and long-tailed [same-store sales] recovery across 2016, and to stress that there is still much work to be done in assessing the sizeable costs associated with the company’s supply chain overhaul.”
For more about food safety crises and product recall, check out the following articles from Risk Management:
Feeding an Appetite for Trust, A Q&A with Center for Food Integrity CEO Charlie Arnot
Food Safety Updates Stalled by Funding
Maximizing Coverage for a Product Recall

 And if that isn’t enough, the report also includes a “Watch List,” calling attention to eight additional jurisdictions “that bear watching due to their histories of abusive litigation or troubling developments.” Those are:
And if that isn’t enough, the report also includes a “Watch List,” calling attention to eight additional jurisdictions “that bear watching due to their histories of abusive litigation or troubling developments.” Those are: But the news isn’t all bad. The report examines “Points of Light,” which are examples of “fair and balanced judicial decisions that adhere to the rule of law and respect the policy-making authority of the legislative and executive branches.” Highlights include positive court rulings from 11 states.
But the news isn’t all bad. The report examines “Points of Light,” which are examples of “fair and balanced judicial decisions that adhere to the rule of law and respect the policy-making authority of the legislative and executive branches.” Highlights include positive court rulings from 11 states.