In February, President Obama issued an executive order instructing the Commerce Department to lead a task force of security experts and industry insiders to develop a voluntary framework to reduce cyberrisk. Last week, the National Institute of Standards and Technology officially released an initial draft of the cybersecurity framework and announced a 45-day open comment period for public input.
The full Preliminary Cybersecurity Framework can be viewed here on the NIST website. After the review period and subsequent revisions, a more complete version will be released in February.
Risk management is a primary focus of the new framework, from the language used to analyze potential exposure to express endorsements in the policy itself. According to a press release, “The Preliminary Framework outlines a set of steps that can be customized to various sectors and adapted by both large and small organizations while providing a consistent approach to cybersecurity. It offers a common language and mechanism for organizations to determine and describe their current cybersecurity posture, as well as their target state for cybersecurity. The framework will help them to identify and prioritize opportunities for improvement within the context of risk management and to assess progress toward their goals.”
Under Secretary of Commerce for Standards and Technology and NIST Director Patrick Gallagher, who was tasked with overseeing development of the framework, emphasized the risk management as a critical component of strengthening national infrastructure in line with the president’s executive order. “We want to turn today’s best practices into common practices, and better equip organizations to understand that good cybersecurity risk management is good business,” Gallagher said.
“The framework will be a living document that allows for continuous improvement as technologies and threats evolve. Industry now has the opportunity to create a more secure world by taking ownership of the framework and including cyber risks in overall risk management strategies.
”
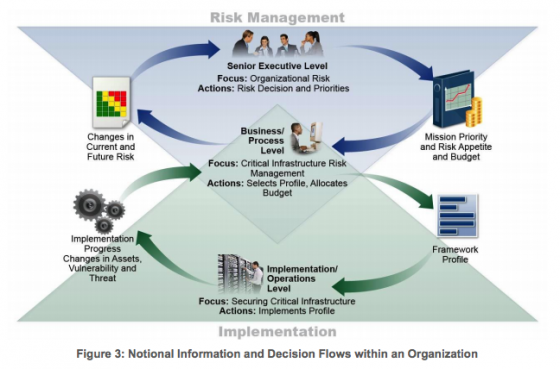
The framework outlines key functions that should organize cybersecurity activities: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover. These functions are designed to aid the risk manager in evaluating, communicating and fortifying against cyberrisks. The document even suggests itself as a potential opportunity for risk managers to seize the opportunity to get involved in proactive cyberrisk strategy. It reads, “The functions also align with existing methodologies for incident management, and can be used to help show the impact of investments in cybersecurity.”
Authors also added the following visual to highlight the critical role of risk management at every level of suggested implementation:
In a blog post, the White House encouraged businesses to evaluate the initial framework and their current cyberrisk position, and to consider their cyber risk appetite in the form of a projected target state for cybersecurity.