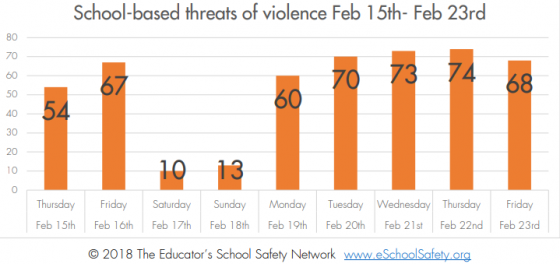
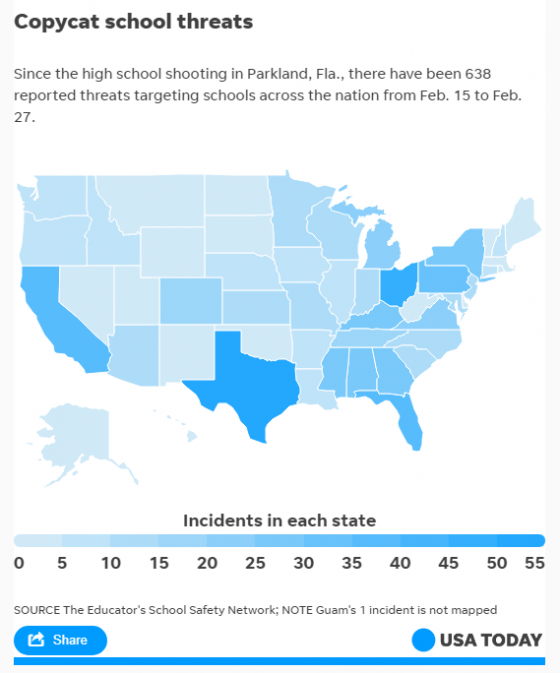
Schools across the country are back in session. And in the wake of high-profile school shootings earlier this year, safety is a top priority for students, parents, educators and communities. Steven Smith, founder and president of Guardian Defense, specializes in active shooter preparedness and works with education industry leaders to keep their facilities safe. 
We reached out to Smith to discuss how preparedness strategies have changed, the types of plans schools implement and for ways to better incorporate them into their culture.
Risk Management Monitor: How have recent school shootings impacted the way you train clients?
Steve Smith: Every mass shooting at a school impacts our training because we learn a little bit more from these horrific events on how to prepare, train and react. Parkland was different for our company because it hit home as this event occurred in our nearby community. Parkland impacted us, our staff, our community and our friends personally. Along with my SWAT Team, I responded to the incident and arrived on scene approximately 30 minutes after the incident. Some of our staff had friends working in the school and knew of other co-workers who had their children attending the school during that time.
RMM: Have they changed active shooter preparedness plans among schools?
SS: By the time law enforcement arrive on scene during a mass casualty incident, the damage has often already been done. The teachers and staff at the schools must receive training, understand the situation, make their own decisions and put action behind it. This will help mitigate mass casualties.
Active shooter preparedness plans change at times depending on the individual school, if they are private, or in a county with a large school district. The biggest hurdle I find in the change in policies is the lack of knowledge and experience. Generally speaking, the “active shooter” concern has not been in school or corporate safety plans for very long. Most administrators tasked with providing training and updating safety plans for this type of threat were never in a formal “lockdown” drill when they were students, themselves. Recognizing this, they rely on the experts for guidance and training to provide them with realistic policies, training and a drill plan for their staff.
RMM: What are the potential risks or benefits of arming teachers?
SS: The perception of every teacher being armed in our schools is not yet a reality in this country. There are alternatives to arming teachers in classrooms. One that immediately comes to mind is training.
A teacher with no previous training will have to incur at least two weeks of firearm training and even more tactical training on how to respond to these incidents. This will take time and money, which is usually hard to come by in any school or business.
Other alternatives that meet safety needs have been discussed and approved in many districts. Schools have hired police officers in their cities to work off-duty employment. This would be my first recommendation because officers are trained and obligated to respond to this threat.
RMM: What are the factors risk professionals should consider when choosing a preparedness plan?
SS: All facets of security are important, such as structural hardening and security upgrades, but if we are building a foundation for active threat preparedness, our recommendation is to follow our model of Policy-Train-Drill.
In order to respond appropriately to a threat on site, every individual needs to understand how to make decisions for themselves and put action behind it. Time is not on our side when it comes to this type of crisis and people, in general, have stood by to wait for direction and instruction when there is an emergency. In these incidents, delayed responses can equate to mass casualties. Therefore, putting the response plans on paper, training all staff, and conducting drills are where we find the best starting point for active threat preparedness.
RMM: When hosting an event, what can risk managers do to avoid a shooting like the recent one in Jacksonville?
SS: If an incident gets to the point where an attacker is carrying out their plan, it does not mean the hosting site failed. In some instances, indications of a threat are not clear or available, making intervention efforts difficult. We can prepare beforehand for a possible threat.
- My first recommendation would be to meet with the local police department and inform them of the event. Request to pay for a detail officer to be on site. The number of hired officers would depend on the projected number of attendees. The officer’s presence alone could deter an attack.
- I would also request to have a meeting with the police supervisor that would be working the day of the event and share the floor plans and emergency procedures with all contact information, so law enforcement and fire would have everything they need in case of an emergency.
- If there are no police available on that day, consider hiring armed security officers to be on site.
- Inside the event site, install a security checkpoint with bag checks or security wands being utilized to ensure no weapons are being brought into the event. Depending on the event, prior notice can be communicated that a strict “no-bag policy” will be enforced.
- Meet with staff beforehand and establish a “safety team” that will discuss vulnerabilities and how you will remedy them.
Regardless of the event, security must be the utmost priority and will at times feel inconvenient for the guests, but the old saying, “Safety first” is how we need to think and prepare in today’s world.